Navigation: Configuration > Configuration Guide (Web Mode) > Configuring Trunks >
Configure intra-office prefixes and outgoing prefixes for unified gateway users so that unified gateway users (intra-office users) can make calls with each other or to external users.
Prerequisites
ϒ⁄Prefixes have been planned.
ϒ⁄The office route selection code has been configured if you need to configure an outgoing prefix. For details, see Configuring an Office Route.
ϒ⁄The number change rule has been configured if it is required. For details, see Configuring the Number Change.
ϒ⁄The number mapping rule has been configured if it is required. For details, see Configuring the Number Mapping.
Context
A call prefix is the string consisting of first few digits or all digits in called numbers.
Prefixes are classified into precise prefixes and wildcard prefixes.
In versions earlier than V2.0, the unified gateway supports only precise prefixes, which can contain only digits 0 to 9, *, #, and +.
In V2.0 and later versions, the unified gateway supports both precise prefixes and wildcard prefixes. In addition to digits 0 to 9, *, #, and +, wildcard prefixes can contain x, [], and [-]. The length of a wildcard prefix must be the same as the number length.
In digit-by-digit collection, if a wildcard prefix contains a precise prefix, the wildcard prefix does not take effect. For example, if prefixes 5 and 5xxx both exist and if a POTS user dials 5000, prefix 5, instead of 5xxx, is matched.
If only precise prefixes are used when number routing rules are complicated, you need to configure a large number of prefixes, increasing the difficulty for deployment and maintenance. In this case, you should use wildcard prefixes.
For example, for number segments where only a middle digit changes, such as 23401, 23411, 23421, ..., 23491, you need to add 10 prefixes if you use precise prefixes. If you use wildcard prefixes, you can add only one wildcard prefix 234x1.
If the called number is 1234, the prefix can be:
ϒ⁄First digit: 1
ϒ⁄First two digits: 12
ϒ⁄First three digits: 123
ϒ⁄Entire called number: 1234
ϒ⁄Wildcard prefix: 1xxx, 1[235]34, and so on
The prefix groups configured on the unified gateway constitute a called number analysis table of the system. If the called number analysis table contains multiple prefixes for a called number, the system uses the maximum matching rule to match the called number with a prefix during number analysis.
Assume that the called number is 1234 and the prefixes 1, 12, and 1234 are configured in the called number analysis table. According to the maximum matching rule, the system will select the prefix 1234, which is the closest to the called number. The prefixes 1 and 12 do not comply with the rule.
The basic service prefixes are classified into two types:
ϒ⁄Intra-office prefix: used for intra-office and outer-office users to call intra-office users. For example, if the intra-office number ranges from 7000 to 7099, you can set the intra-office prefix to 7. When calling an intra-office user, you can simply dial the user number such as 7001.
ϒ⁄Outgoing prefix: used when intra-office users make outgoing calls, such as local calls, national toll calls, or international toll calls. For example, when intra-office user 7000 makes a call to outer-office user 12345678, the following scenarios are available:
Figure 1 shows the scenario where number change is not involved.
Figure 1 Scenario not involving number change
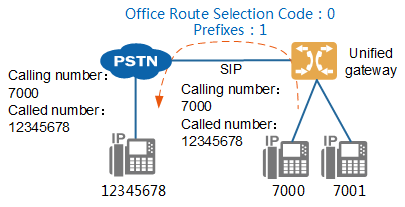
If number change is involved, see Configuring the Number Change for how to configure number change. Figure 2 shows the scenario where number change is involved. This scenario assumes that the number change rule deletes the first digit 9 of the called number and prefixes the calling number with 5.
Figure 2 Scenario involving number change
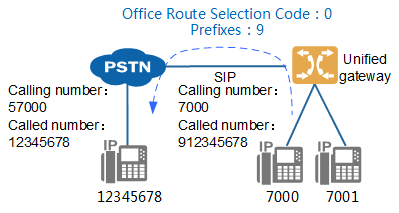
![]()
Prefix configuration is flexible. It is up to the users' dialing habits and the number plan.
Table 1 Prefix Description
Prefix Type |
Value |
Remarks |
Digits |
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 |
None |
Symbols |
Asterisk (*), number sign (#), and plus sign (+) |
The asterisk can be the first or last character only. The number sign can be the first or last character only. The plus sign can be the first character only. NOTICE: A prefix configured for call barring cannot start with an asterisk (*) or a pound sign (#). |
Wildcard |
Wildcard x indicates any digit of 0-9. |
To avoid abnormal outgoing calls, wildcard x cannot be the first character in a prefix. Wildcard x cannot appear in []. A wildcard is case-insensitive. Therefore, x and X are the same. |
Range |
The characters in [] must digits 0-9 only. Any character inside [] can be matched. For example, [0125] matches any digit of 0, 1, 2, and 5. |
[] must appear in pairs and cannot contain []. There must be at least one character in []. Digits in [] must appear in ascending order. |
Sub-range |
Two digits before and after a hyphen (-) together indicates a range, for example, 2-4 can match any digit from 2 to 4. The form of two digits before and after a hyphen must appear in []. For example, [1-578] indicates digit 7 or 8 or any digit from 1 to 5. |
A hyphen (-) must appear in [], the characters before and after it must be digits only, and the digit before the hyphen must be smaller than the digit after the hyphen. For example, [01-34] is correct, but [10], [1], [], [-], [-9], [3-3], and [3-2] are incorrect. |
Table 2 give some examples of wildcard prefixes.
Table 2 Wildcard prefix examples
Example |
Description |
[2-8]xxxxxxx |
This prefix matches an 8-digit number. The first digit is any digit from 2 to 8, and each of the rest seven digits is one from 0 to 9. |
13xxxxxxxxx |
This prefix matches an 11-digit number. The first digit must be 1, the second digit must be 3, and each of the rest nine digits is one from 0 to 9. |
1[0124-9]x |
This prefix matches a 3-digit number. The first digit must be 1, the second digit can be 0, 1, 2, or one from 4 to 9, and the third digit is any digit from 0 to 9. |
In versions earlier than V200R003C30SPC100, Wildcard prefixes support only called prefix analysis. Calling prefix analysis and trunk bearer prefix analysis are not supported. In addition, wildcard prefixes support only the following four basic services: intra-office call, local call, national toll call, international toll call, and localinter.
The wildcard prefix number analysis table is independent of the precise prefix number analysis table. When analyzing a number, the unified gateway searches the precise prefix number analysis table first. If the corresponding prefix exists and the analysis result is precise exact match, searching ends; otherwise, the unified gateway searches the wildcard prefix number analysis table. If a wildcard prefix with exact match exists, this wildcard prefix prevails; otherwise, the analysis result of the precise prefix number analysis table is used.
When two wildcard prefixes are matched, the one with more precise match prevails. For example, for wildcard prefixes 31xx and 310x, if number 3100 is dialed, wildcard prefix 310x prevails. This is because wildcard prefix 310x contains 10 prefixes and 31xx contains 100 prefixes. In the case of the same match level (for example, 31x0 and 310x), the one appearing first in the show prefix command output prevails.
In V200R003C30SPC100 and later versions, wildcard prefixes support called prefix analysis and calling prefix analysis.
Scenario Description
This topic assumes that you want to:
ϒ⁄Add intra-office prefix 7 and set Service type to Basic service.
ϒ⁄Add outgoing prefix 9 and set the office route selection code to 0, Service type to Basic service, and Call property to Local call.
![]()
To prevent toll fraud, before adding the local call prefix, you must add the national toll call prefix and international toll call prefix; otherwise, the local call prefix cannot be added.
Procedure
1.Configure the intra-office prefix.
a.Log in to the web management system. For details, see Logging In to the Web Management System.
b.Choose Trunk > CalleePrefix Configuration and click Create.
c.Configure a prefix in the Create Prefix dialog box, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Configuring an intra-office prefix
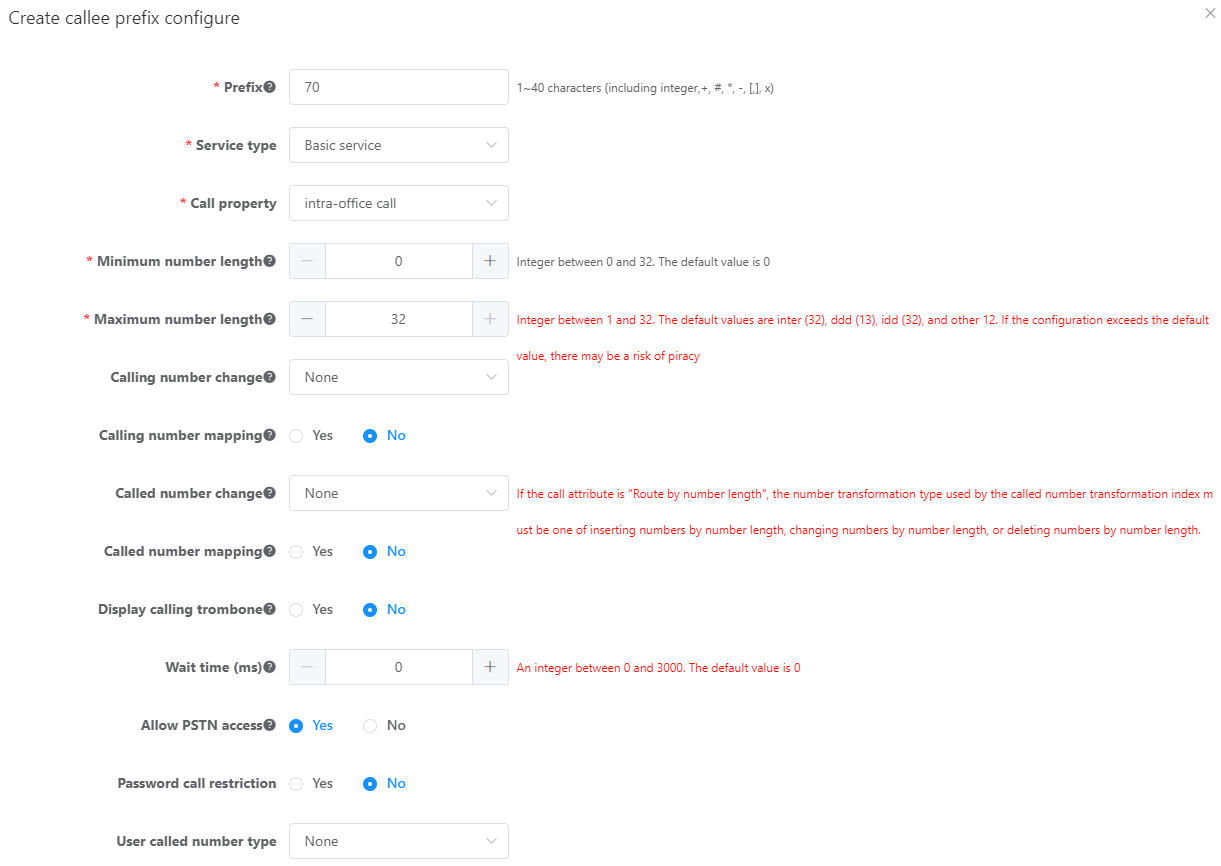
Table 3 describes the key parameters displayed on the page. For detailed description about the parameters, see the Web Management System Online Help.
Table 3 Key parameter description
Parameter |
Description |
Prefix |
A wildcard prefix cannot exceed 40 characters, and the actual prefix cannot exceed 32 characters. For example, wildcard prefix 3[3-6] contains six characters, and the matched actual prefix contains two characters. |
Service type |
ϒ⁄Basic service The service type is a basic audio service such as intra-office call and local call. ϒ⁄Supplementary service The service type is a supplementary service. ϒ⁄Intelligent service The service type is a common intelligent service, and is currently unavailable. ϒ⁄SoftConsole service The service type is a softconsole service such as the call waiting and attendant group in the console. ϒ⁄Virtual user The service type is a virtual user service such as the phone meeting, automatic switchboard, and customized VU. ϒ⁄Card number service The service type is a card number service such as the call, recharge, password change, balance query, terminal binding, prepaid, or postpaid service. ϒ⁄Call by Dialing Card NumbeSr Users can dial a card number to make intra-office calls, national toll calls, international toll calls, and emergency calls. |
Call property |
ϒ⁄Intra-office call This option is selected for calls between users under the same unified gateway. ϒ⁄Local call This option is selected for local calls. ϒ⁄National toll call This option is selected for national toll calls. ϒ⁄International toll call This option is selected for international toll calls. ϒ⁄Emergency call This option is selected for emergency calls, for example, to 911. ϒ⁄Intra-office or local call This option is selected when first digits in a local number compose a short number. The call with this attribute is routed to the intra-office user. If the routing fails, the call is then routed to the local user in another office. ϒ⁄Route by number length This option is selected for outgoing calls with the same prefix but with different number lengths. For details, see Add a number route analyzing prefix. ϒ⁄Local regeneration call This option is selected for calls between intra-office users and local PSTN users when both active and standby devices in the centralized call management network mode fail and the local generation function is enabled. |
Calling number change |
Index of a calling number change rule. The calling number change rule is used to change calling numbers, for example, to a switchboard. The priorities of the three number change modes are long number and short number, number mapping, and number change in descending order. For details, see Configuring the Number Change. |
Calling number mapping |
Indicates whether to display the mapping number of a calling number. If a user is not configured with the long number, the mapping number is displayed on the called parties' phones. The priorities of the three number change modes are long number and short number, number mapping, and number change in descending order. For details, see Configuring the Number Mapping. |
Called number change |
Index of a called number change rule. For example, a called number change rule can be as follows: If the calling party dials 912345678, unified gateway deletes the outgoing prefix 9 and sends the called number 12345678. The priorities of the three number change modes are long number and short number, number mapping, and number change in descending order. For details, see Configuring the Number Change. |
Called number mapping |
Indicates whether the mapping number of a called number can be used in dialing. If a user is not configured with the long number, the mapping number can be used. The priorities of the three number change modes are long number and short number, number mapping, and number change in descending order. For details, see Configuring the Number Mapping. |
Display long calling number |
The long number is a number used for short-number users to make outgoing calls or for outer-office users to call short-number users. The default value is No. When the parameter is set to Yes and the user is configured with a long number, the calling number is changed to the long number for outgoing calls. The priorities of the three number change modes are long number and short number, number mapping, and number change in descending order. |
PSTN access |
Indicates whether to allow trunk users to call the prefix. When the parameter is set to No, trunk users cannot call numbers starting with the prefix. |
User called number type |
(For digital trunks) Type of the called number sent to the PSTN when an intra-office user makes an outgoing call using the prefix. |
User calling number type |
(For digital trunks) Type of the calling number sent to the PSTN when an intra-office user makes an outgoing call using the prefix. |
Change the trunk called number type |
(For digital trunks) Indicates whether to change the called number type when an outgoing tandem call is made using the prefix. |
Trunk called number type |
(For digital trunks) Type of the called number sent to the PSTN when an outgoing call is made using the prefix. |
Change the trunk calling number type |
(For digital trunks) Indicates whether to change the calling number type when an outgoing tandem call is made using the prefix. |
Trunk calling number type |
(For digital trunks) Type of the calling number sent to the PSTN when an outgoing call is made using the prefix. |
Call Source |
In V2.0 and later versions, if Service type is Basic service and Call property is Intra-office or local call or Local regeneration call, the Call Source configuration item is added on the UI. This configuration item is used to process the long-number calls of analog users on the local node, preventing a cyclic route between the local node and the central node for such calls. |
32-level customized rights |
32-level customized rights that are extended based on basic all rights. Customized rights can be used with prefix rights to restrict calls. For example, if the cus1 customized right is configured for outgoing prefix 9 and user 7000, only user 7000 can dial prefix 9 to make outgoing calls. |
![]()
ϒ⁄The User called number type, User calling number type, Change the trunk called number type, Trunk called number type, Change the trunk calling number type, and Trunk calling number type parameters are used to change the calling and called number type based on the called number prefix for outgoing calls through the E1 trunk ( ISUP, PRI, and QSIG, R2 not supported). The types include User Number, National Number, International Number, and Unknown.
ϒ⁄You can configure the maximum number length for a prefix when adding the prefix. By default, the maximum number length is 32. To prevent unauthorized users from making toll fraud calls by adding number prefixes, you are advised to configure different number lengths based on the prefix type. In the V200R003C50SPC300 and later versions, the default maximum number lengths are as follows: 32 for intra-office calls, 13 for national toll calls, 32 for international toll calls, and 12 for local calls, local regeneration calls, local inter-office calls, and intra-office or local calls.
b.Click OK.
2.Configure the outgoing prefix.
Add the national toll call prefix and international toll call prefix before adding a local call prefix. If not, the operation of adding a local call prefix fails.
a.Click Create on the prefix configuration page.
b.Configure a prefix in the Create Prefix dialog box, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Configuring an outgoing prefix
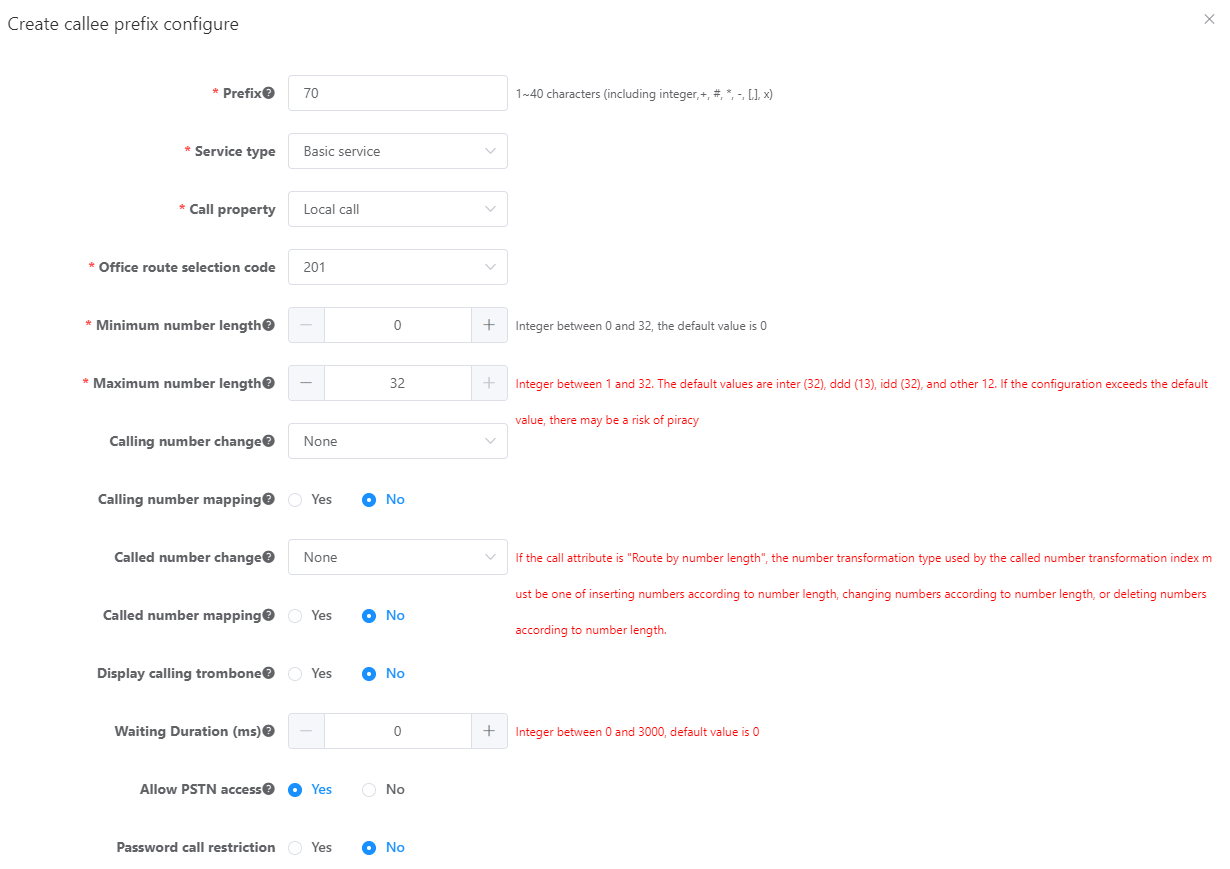
Table 3 describes the key parameters displayed on the page.
c.Click OK.
3.Click Data Save in the upper right corner of the web management system.
![]()
The unsaved configurations will be deleted after the device is restarted.
Result
Log in to the web management system, choose Trunk > Called Prefix Configuration, and query configured precise prefixes and wildcard prefixes.
Parent Topic: Configuring Trunks