Navigation: Configuration > Configuration Guide (Web Mode) > Configuring Trunks > Configuring Signaling Data >
This topic describes how to configure a PRA trunk connection between the unified gateway and the peer device.
Prerequisites
ϒ⁄For the X1911/X1960/X1981
ϒ⁄You have installed the digital trunk cable that connects the local office and the peer office. For details on how to install the digital trunk cable, see the Quick Installation Guide.
Context
PRA trunk
A PRA trunk is a digital circuit trunk that is connected to the peer device through the E1 or T1 trunk cable. The PRA trunk uses the Digital Subscriber Signaling No.1 (DSS1) as the control signaling. The DSS1 is designed based on the network/user model. That is, one side of the trunk is the network, and the other side is the user.
Clock source
The clock source is configured on one device so that the peer device can synchronize its clock with this device. The configuration of a clock source prevents the frame slip (voice packet loss).
ϒ⁄If the unified gateway connects to multiple devices through E1 or T1 trunks, configure the clock source on any of these devices. The unified gateway will synchronize time with this device.
ϒ⁄If the unified gateway provides the clock source, you do not need to configure a clock source.
Scenario Description
Configurations vary depending on the actual data plan. The following assumes that you need to:
Using the X1960 as an example, add a PRA link. Set the office route number to 0, link number to 0, E1/T1 port number to 0, and link position to User Side.
Procedure
1.Log in to the web management system. For details, see Logging In to the Web Management System.
2.Configure a PRA trunk.
a.Choose Trunk > Trunk Configuration > PRA from the navigation tree.
![]()
The system has a default local office Local.
b.Click Add A Peer Office in the PRA trunk configuration area.
The blue icon point:0 (the peer device) is displayed.
c.Click point:0 or the line between the local office and the peer device.
d.Click Create on the page that is displayed.
e.Set the parameters according to actual situations and the parameter description on the page, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Configuring a PRA trunk
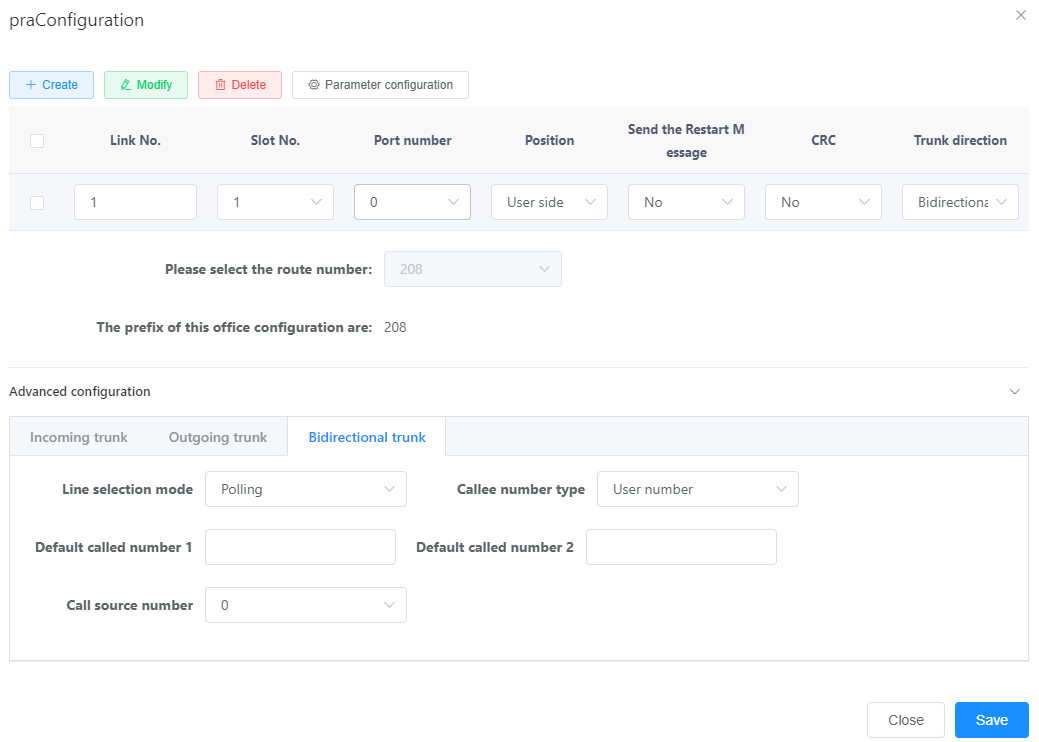
Table 1describes the key parameters displayed on the page. For detailed description about the parameters, see the Web Management System Online Help.
Table 1 Key parameter description
Parameter |
Description |
Position |
Position in a PRA link. The options are User Side and Network Side. |
Link Timeslot |
Circuit ID of a link, which specifies the timeslot in the E1 or T1 link of a PRA trunk. When E1 is used, this parameter can be set only to 16. When T1 is used, the value of this parameter is an integer ranging from 1 to 24. |
CRC |
CRC is a data verification mechanism. The values of the local office and peer office must be the same. If the peer office enables the CRC, set this parameter to Yes. |
Whether to send the abnormal tone |
Indicates whether to play an announcement based on the returned cause code when you hang up. If this parameter is set to No, the system plays a tone when you hang up. The default value is Yes. |
f.Click OK.
When the PRA trunk configuration is complete, the line between the local office and the peer office turns green.
A green line indicates a successful data configuration, while a red line indicates that the data is not configured or the configuration fails.
3.Configure a clock source. For details, see Configuring a Clock Source.
Verification
Task |
Operation |
Result |
Verify the trunk connection. |
An intra-office user calls an outer-office user. |
The call is successful. |
Troubleshooting
If the call fails, see Trunk Faults.
Parent Topic: Configuring Signaling Data