Navigation: Configuration > Configuration Guide (Web Mode) > Configuring Trunks > Configuring Signaling Data >
This topic describes how to configure a SIP trunk connection between the unified gateway and the peer device. The peer device must support the SIP trunk.
Context
The SIP trunk is a packet trunk based on the IP network. It is connected to the peer device through the Ethernet cable.
Different from a physical channel defined by a circuit trunk, a SIP trunk defines a logical channel, which solves the issues about interoperability authentication and call addressing between the local office and the peer office.
The following transmission protocols can be used for unified gateway.
Protocol |
Description |
Local Port |
UDP |
A connectionless transport layer protocol that provides a simple but unreliable transaction-oriented information transmission service. UDP features less resource consumption and higher processing speed, but does not guarantee that data packets can be sent to the destination safely and completely. |
5060 (mandatory) |
TCP |
A connection-oriented, reliable IP-based transport layer protocol. The processing speed of TCP is lower than that of UDP, but TCP supports retransmission of lost packets and data verification to ensure that data packets can be sent to the destination safely and completely. |
5060 (recommended) |
TLS |
A cryptographic protocol that provides communication security between two communication application programs, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. |
5062 or 5063 (recommended) |
This topic describes how to configure a SIP trunk that uses the non-cryptographic UDP or TCP protocol. To acquire higher security, you can configure a SIP trunk using TLS by referring to Configuring Signaling Encryption.
Scenario Description
Configurations vary depending on the actual data plan. The following assumes that you need to:
Configure the SIP trunk. Set the office route number to 0, domain name of the peer device to pbx1, IP address of the peer office to 172.16.15.87, transmission protocol to UDP, signaling port number of the local and peer offices to 5060.
Procedure
1.Log in to the web management system. For details, see Logging In to the Web Management System.
2.Choose Trunk > Trunk Configuration > SIP from the navigation tree.
3.Click Add A Peer Office in the SIP trunk configuration area.
The blue icon point:0 (the peer device) is displayed.
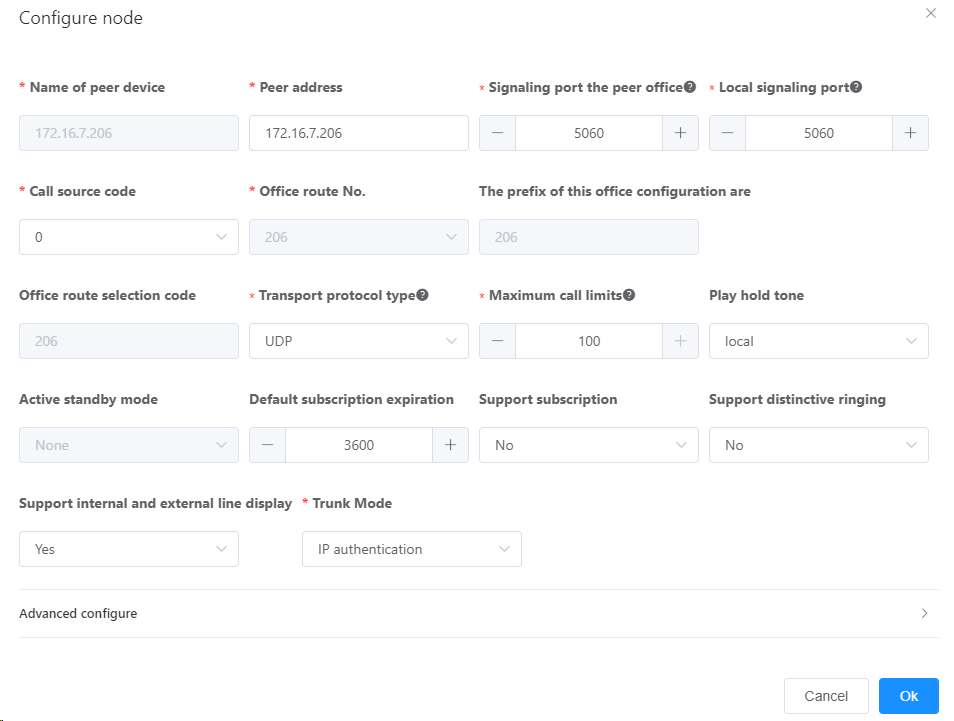
4.Click point:0 or the solid line between the local office and point:0, and set the parameters according to actual situations and the parameter description on the page, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Configuring a SIP Trunk
![]()
If you use a TCP port that is not 5060 in SIP trunk communication, configure an FPGA flow control rule based on the transmission protocol for the port, and set the data transmission flow control threshold to 1000 to prevent traffic attacks on the port. For details, see Traffic Control.
Table 1describes the key parameters displayed on the page. For detailed description about the parameters, see the Web Management System Online Help.
Table 1 Key parameter description (2)
Parameter |
Description |
Domain name of the peer device |
Domain name that uniquely identifies a peer device. This parameter is mandatory, and the domain name must be unique. |
Transmission protocol type |
There are four types: UDP, TCP. TLSServer and TLSClient. NOTE: If you want to encrypt signaling using TLS, configure the communication parties as TLSServer and TLSClient respectively. For details, see Configuring Signaling Encryption. |
Select office route number |
ID of the office route that a SIP trunk belongs to. |
Maximum number of restricted calls |
Maximum number of calls on a SIP trunk. If the number of incoming and outgoing calls routed through a SIP trunk exceeds the maximum number, the system automatically rejects new calls. |
5.Click OK.
When the SIP trunk configuration is complete, the line between the local office and the peer office turns green.
A green line indicates a successful data configuration, while a red line indicates that the data is not configured or the configuration fails.
6.Click Data Save in the upper right corner of the web management system.
![]()
The unsaved configurations will be deleted after the device is restarted.
Verification
Task |
Operation |
Result |
Verify the trunk connection. |
An intra-office user calls an outer-office user. |
The call is successful. |
Troubleshooting
If the call fails, see Trunk Faults.
Parent Topic: Configuring Signaling Data