Navigation: Configuration > Configuration Guide (Web Mode) > Allocating User Numbers >
This topic describes how to allocate numbers to SIP users on the unified gateway to enable SIP users to make outgoing calls and receive incoming calls. SIP users refer to users who use IP phones, UScale soft terminals, and POTS phones connected to UScale Integrated Access Devices (IADs).
Prerequisites
ϒ⁄User numbers have been planned for the unified gateway.
ϒ⁄Initial configurations (such as IP address configuration) have been performed on IP phones or IADs if SIP users use IP phones or POTS phones connected to the IADs.
Context
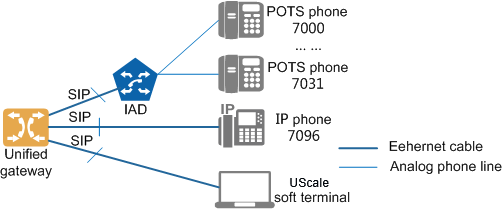
SIP users use SIP to communicate with a SIP server for call connection. On the unified gateway, SIP user devices can be IP phones, UScale soft terminals, and POTS phones connected to UScale IADs. The unified gateway functions as a SIP server that receives registration and call requests from SIP users. Figure 1 shows the network involving SIP users.
Figure 1 Unified gateway network involving SIP users
The unified gateway supports batch and single number allocation. You can select an allocation mode based on the number plan. If you select the batch mode, the unified gateway allocates numbers in batches based on the specified start number, number step, and number count.
The unified gateway supports four user right levels. You can configure different right levels for different users to control the service and call rights of users.
ϒ⁄Table 1 lists the service rights for different user right levels.
Table 1 Service rights for different user right levels
User Right Level |
Service Rights |
Default |
Users of this level have rights to use the local number query, call transfer, call forwarding, call waiting, abbreviated dialing, call-out barring, alarm clock, CLIP, password change, phone meeting, unified fax mailbox, call park, phone permission, ONLY, DND, multi-call, instant meeting and absent user services. |
Common |
In addition to service rights for the Default right level, users of this level have rights to use the RCB(only for POTS users), CBB, designated pickup, and group pickup services. |
Advanced |
In addition to service rights for the Normal right level, users of this level have rights to use the three-way calling, ringing, break-in, forced release, hotline, CTVMU, CTVMB, CTVMNR, CTFMU, CTVMO, call forwarding presence, call forwarding conditional, callback on no reply, and BLF services. |
Super |
In addition to service rights for the Advanced right level, users of this level have rights to use the privileged user, secretary, secretary station services. |
ϒ⁄Table 2 lists the call rights for different user right levels.
Table 2 Call rights for different user right levels
User Right Level |
Intra-Office Call |
Local Call |
National Toll Call |
International Toll Call |
Default |
√ |
√ |
× |
× |
Common |
√ |
√ |
Only working time |
× |
Advanced |
√ |
√ |
√ |
Only working time |
Super |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
To meet common users cannot make national toll calls, and advanced users cannot make international toll call in non-working hours, on the basis of the PIN-Code call barring service, the config set workingtime switch switch starttime starttime endtime endtime directdialtmpright on command can be executed on the unified gateway to set the working time and enable the temporary toll call rights. In this way, common user can make national toll calls and an advanced user can make international toll calls in non-working hours. For details.
![]()
During number allocation, you must specify the SIP device IDs (used as registered accounts of SIP users) and authentication modes, and ensure that the settings for these parameters are the same on the SIP user side and the unified gateway.
Scenario Description
This topic uses the following scenario as an example to describe how to allocate numbers to SIP users. You must allocate numbers based on the actual number plan.
ϒ⁄You need to configure 32 SIP users who use POTS phones connected to an IAD. The user numbers range from 7000 to 7031.
ϒ⁄You need to configure one SIP user who uses an IP phone. The user number is 7096.
ϒ⁄All SIP users have rights of the Default user right level and use password authentication.
Figure 2 shows the process of allocating numbers to SIP users based on the preceding requirements.
Figure 2 SIP user number allocation process
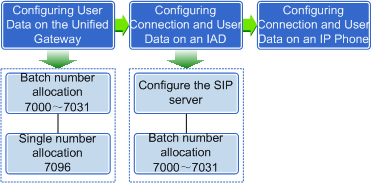
Configuring User Data on the unified gateway
1.Log in to the web management system. For details, see Logging In to the Web Management System.
2.Choose User > SIP User and click Create on the SIP User page.
3.Enter user information on the Add SIP User page that is displayed, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Batch Adding SIP Users
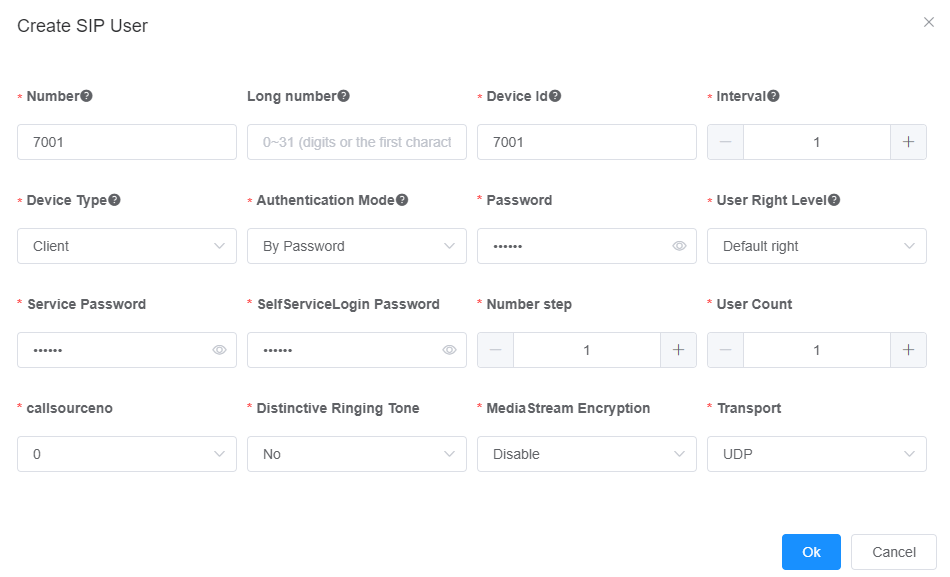
Table 3 describes the key parameters.
Table 3 Key parameter description
Parameter |
Description |
Account |
SIP user ID used in authentication. The value is the same as the SIP device ID configured on the unified gateway. |
User Name |
Account name provided by the VoIP service provider. The value is similar to or is a phone number. It is the same as the user number configured on the unified gateway. |
Password |
Indicates the password used for an account to register with the SIP server. Set this parameter to the authentication password for the SIP user configured on the unified gateway. In X1900 V2.0 or a later version, the password can be changed on the Self-service > ONLY page for the unified gateway self-service platform. |
Server 1 |
IP address of the SIP server. Set this parameter to the IP address of the unified gateway. |
Port |
Port number of the SIP server. NOTE: ϒ⁄If TLS is selected, the default value of this port is 5061. ϒ⁄If UDP or TCP is selected, the default value of this port is 5060. |
|
|
|
|
Figure 4 SIP User page

You can select one user and click ![]() to modify user information, or click Delete to delete the users.
to modify user information, or click Delete to delete the users.
1.Add SIP user 7096, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Adding a SIP user

2.Click OK.
The SIP User page is displayed. If you want to modify or delete users.
Parent Topic: Allocating User Numbers