Navigation: Fault Management > Troubleshooting Guide > Call Faults >
This topic describes how to rectify basic voice call faults, for example, call failures and exceptions.
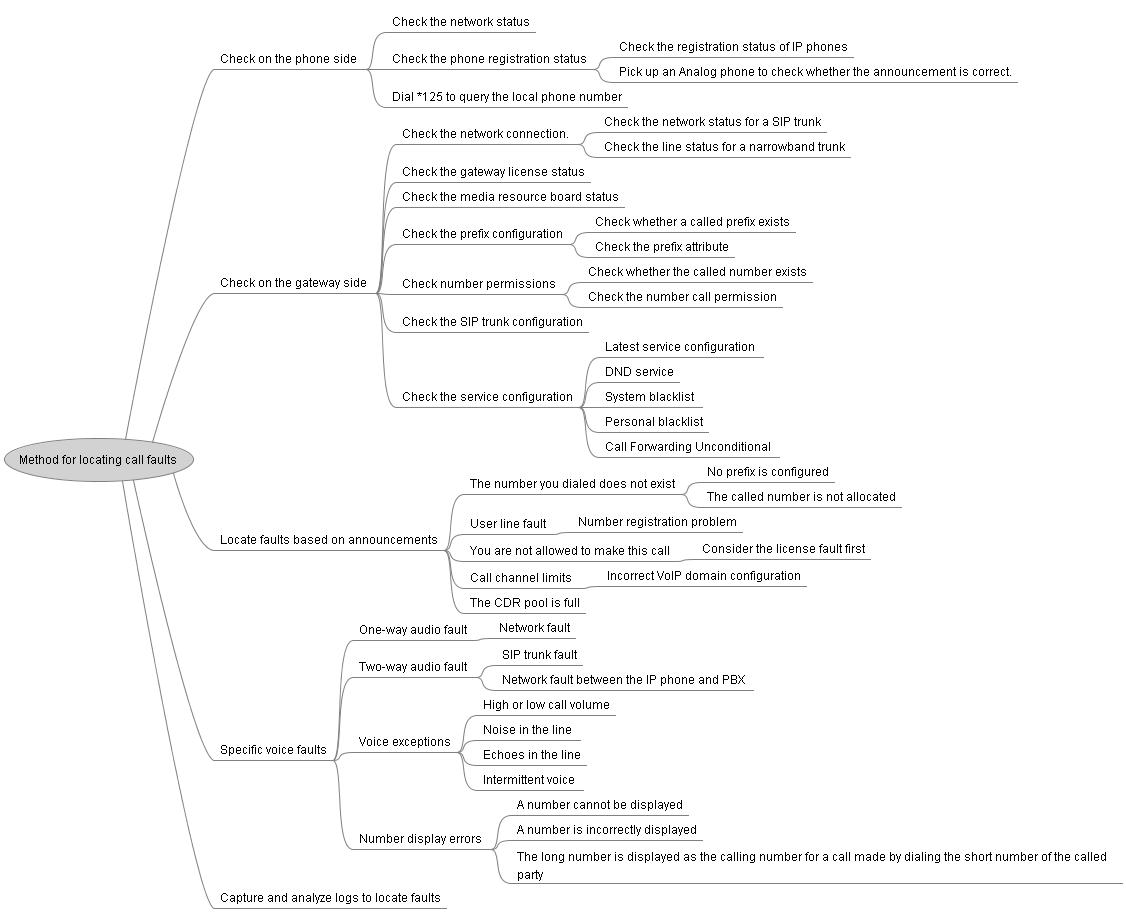
Figure 1 Method for locating call faults
Checking the Network Status
Use the ping command to check the network status, delay, and packet loss between the unified gateway and phone.
Checking the Phone Registration Status
The announcement "Sorry, the number you dialed cannot be reached at this time due to line faults." is played when you make a call if the registration status of the called party's phone is abnormal.
ϒ⁄Check the registration status of an IP phone.
ϒ⁄Pick up the phone to check whether the announcement is correct.
The IDLE state indicates that phone registration status is normal.
For details about how to rectify the phone registration failure, see the first special theme "Login and Registration."
Dialing *125 to Query the Local Phone Number
Dial *125 on phone A. The announcement "Your number is xxx." is played properly, which indicates the following:
ϒ⁄The phone and gateway are corrected properly.
ϒ⁄The gateway plays the announcement properly; that is, the gateway status is normal.
The announcement "Your number is xxx." is played by the unified gateway to phones. If announcement playback is abnormal, the status of the media resource board on the gateway is abnormal.
Checking the Gateway License Status
License exceptions or expiration causes call failures.
Log in to the web management system of the UScale X1900 unified gateway as the administrator, choose System > License Information, and view information about the unified gateway license.
Figure 2 License information

The license State should be Valid, and Run LeftDays should not be 0.
Checking the Media Resource Board Status
The media resource module of the UScale X1900 unified gateway is located in the media trunk unit (MTU) and responsible for functions listed in the following figure.
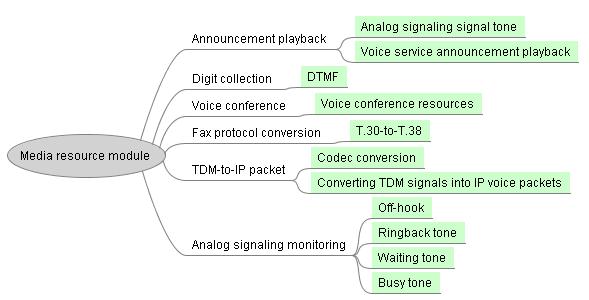
When receiving an INVITE message, the unified gateway sends an instruction to the MTU based on the judgment result to instruct it to play the corresponding signal tone.
If the MTU status is abnormal, announcements will fail to be played.
Table 1 Announcement playback types
Terminal |
Announcements Stored On |
Off-Hook Dialing Tone |
Ring Tone |
Ring Back Tone (Default) |
Ring Back Tone (RBT) |
Voice Service Announcement |
IP phone |
Phone |
Played by the phone |
Played by the phone |
Played by the phone |
Played by the gateway |
Played by the gateway |
POTS phone |
Unified gateway |
Played by the gateway |
Played by the gateway |
Played by the gateway |
Played by the gateway |
Played by the gateway |
Check the MTU status as follows:
1.Log in to the web management system of the UScale X1900 unified gateway as the administrator.
2.Choose Resource > Board Status, and check the MTU status indicator.
Alternatively, you can run the show board command.
If board faults or alarms exist, rectify them in a timely manner.
Checking the Prefix Configuration
The announcement "Sorry, the number you dialed does not exist. Please check the number and dial again." will be played if no called prefix is configured. Incorrect call attributes of a prefix will also cause call failures.
Log in to the web management system of the UScale X1900 unified gateway, choose Trunk > Prefix Configuration, check whether the called prefix exists, and check call attributes of the prefix. The intra-office call attribute should ne inter, and the outgoing call attribute should be Local, DDD, or IDD.
Alternatively, you can run the show prefix dn command to query the prefix.
Checking Whether the Called Number Exists
1.Log in to the web management system of the UScale X1900 unified gateway as the administrator.
2.Choose User > SIP User or User > POTS User, and check whether the called number exists. If no, click Create to configure the called number.
Checking the Number Call Permissions
If the calling number does not have the outgoing call permission or the called number does not have the corresponding incoming call permission, call failures occur.
1.
Disable the DND service for the called number, and check whether the call function is normal.
ϒ⁄Pick up the phone and dial #56#. An announcement is played, indicating that the service is deregistered successfully.
ϒ⁄Alternatively, press the DND softkey on the lower screen of the IP phone for which DND is enabled to deregister DND. DND enabled is no longer displayed on the lower screen of the IP phone.
Checking the System Blacklist and Whitelist
The system blacklist and whitelist are used to shield specific calls (for example, ad sales calls) or restrict all users from calling specific numbers (for example, premium-rate telephone number).
The UScale X1900 unified gateway adds users to different call barring groups including the blacklist group, whitelist group, and common call barring group to control call permissions of users.
The following figure shows call permissions of users in different call barring groups.
Figure 3 System blacklist and whitelist call permissions
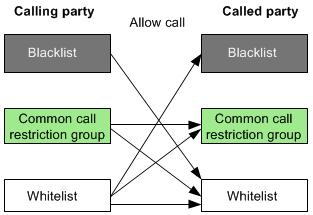
Check the calling party blacklist and whitelist, and find that calling number 4000 is in the system calling party blacklist.
According to call permissions shown in Figure 3, a number in the calling party blacklist cannot make calls to a number in the called party blacklist. Therefore, calling number 4000 will fail to make calls to called number 5000.
Checking the Personal Blacklist
A user can configure the personal blacklist to reject calls from users in the blacklist. When a user in the blacklist makes a call to this user, the system plays the call barring announcement.
![]()
The personal blacklist priority is lower than the system blacklist and whitelist priorities.
Check the personal blacklist:
ϒ⁄Log in the web self-service system of the UScale X1900 unified gateway using number 5000, choose Self-service > Service > Blacklist, and find that calling number 4000 is in the blacklist of called number 5000. This is the call failure cause.
ϒ⁄Alternatively, run the following command:
![]()
BlackDn indicates a user in the blacklist of the user identified by UserDn. The user specified by BlackDn cannot make calls to the user specified by UserDn. A maximum of 10 blacklisted users can be added for a user.
Delete number 4000 from the blacklist of number 5000. The call can be made successfully.
Checking Whether CFU Is Enabled for the Called Party
Check whether the call forwarding unconditional (CFU) service is enabled for called number 5000 and whether the forward-to number is valid. If the forward-to number is invalid, the call fails.
Log in the web self-service system of the UScale X1900 unified gateway using number 5000, choose Self-service > Service > Forwarding service, and disable Number for Forwarding unconditional.
Parent Topic: Call Faults