Navigation: Fault Management > Emergency Maintenance > Quick Troubleshooting >
Check whether the hardware device and the bearer network are functioning properly and whether the configuration data is correct when partial service is congested.
Context
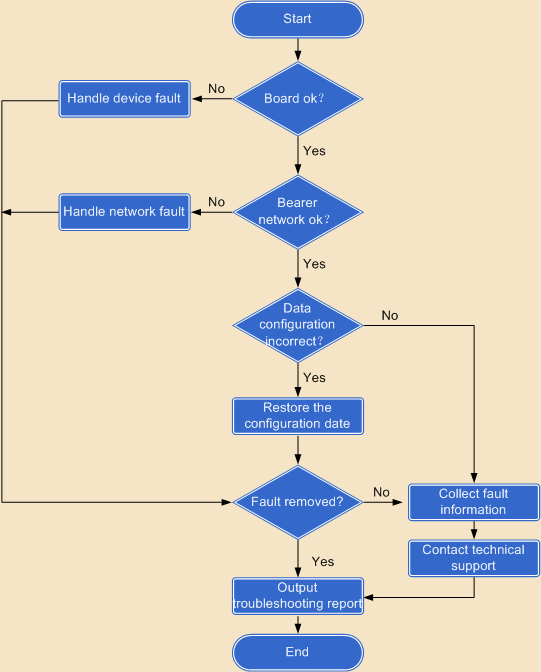
When partial service congestion occurs, you can rectify the fault by checking the hardware device, network, and configuration data in sequence. Figure 1 shows the process of handling partial service congestion.
Figure 1 Process of handling partial service congestion
Symptom
Partial service is congested in any of the following conditions:
ϒ⁄Some media gateways fail to register with the network, for example, being disconnected immediately after they are registered.
ϒ⁄Calls are congested on some user terminals. For example, users fail to make or receive calls, and fail to hear the dial tone or busy tone after they hang up the phone.
ϒ⁄Calls are congested in some office directions. For example, users fail to make or receive calls.
Impact Scope
The services in some areas are interrupted or congested for a long time on the unified gateway.
Procedure
1.Check whether any board crashes.
If some boards of the unified gateway crash, handle the fault as described in Handling a Board Crash immediately.
2.Check whether the bearer network is functioning properly.
Use the ping command to check whether the unified gateway successfully communicates with the congested gateway. For details, see Checking Network Status.
If the communication between the unified gateway and the media gateway, terminals, or other switches is abnormal, handle the bearer network fault.
3.Check whether the partial service congestion is caused by modification of configuration data.
When the unified gateway is running, do not modify configuration data. If configuration data is modified, the system may fail to work.
4.Check whether the fault is rectified.
a.If the fault is rectified, proceed to 6.
b.If the fault is not rectified, proceed to 5.
5.Obtain technical support.
If you fail to rectify the fault following the emergency fault handling process, collect related fault information and contact your service provider for technical support.
6.Output a fault handling report.
Parent Topic: Quick Troubleshooting