Navigation: Configuration > Configuration Examples in Typical Scenarios > Configuring the Unified Gateway Two-Node Cluster >
This topic describes how to configure the local nodes in a multi-node centralized call management network for the unified gateway two-node cluster.
Prerequisites
Basic data, including the unified gateway IP address, boards, and time zone, has been configured for the local node. For details, see Configuring the Basic Information.
![]()
In V2.0 and later versions, you must change the Data synchronize password before configuring the connection between the central and local nodes; otherwise, the connection fails.
Configuring Distributed Network Data
1.Use an administrator account to log in to the web management system of a X1900 series unified gateway.
2.Choose System > Network Mode.
3.Configure the active node and standby node, For parameter description, see X1900 series unified gateway web help.
![]()
ϒ⁄When the active node deploys the X1900, it is recommended that you use the same value for Active node trunk port number and Active node register port number.
ϒ⁄When DataSynMode is DB, Active node authentication password is mandatory.
4.Click OK.
For details about how to check the status of the connections between the local nodes and the active node and between the local nodes and the standby node, see Verifying the Connection Status.
5.Modify Data synchronize password.
Choose System > Device Management, modify Data synchronize password.
The data synchronize password is used for data synchronization between the primary gateway and the local gateway. You can customize the password, but the password configured on the local gateway must be the same as that configured on the primary gateway. Otherwise, data synchronization will fail.
Configuring User Data
The process of configuring user data for branch 1 is similar to that for branch 2. The following describes how to configure user data for branch 1:
1.Configure SIP users (IP phones, and POTS phones and fax machines under IADs) at branch 1.
SIP users at branch 1 have been configured on the central node, and SIP user numbers have been synchronized to the local node, so user numbers do not need to be allocated to the SIP users on the local node.
2.Configure POTS users (POTS phones and fax machines directly connected to the local node) at branch 1.
a.Choose User > POTS User and click Create.
b.Configure two POTS users with numbers 85000 and 85001 (without long numbers).
![]()
From V200R003C30SPC300, two additional parameters, namely Service password and Self-service login password, are provided for a user being created. You can log in to the web management system and configure Service password and Self-service login password, or run the config system subscriber defaultpwd password password webpassword webpassword command in global config mode to configure the default service password and self-service login password for the user. If the passwords are not configured using either the command or web management system, the user fails to be created. If the passwords are configured using both the command and web management system, the configurations in the web management system prevail.
c.Click OK.
Configuring Office Route Data
1.Set office route selection codes.
ϒ⁄The office route selection code is 0 when local node 1 connects to the PSTN through a PRA trunk.
ϒ⁄The office route selection code is 252(X1911/X1960)or 1021 (X1981) when local node 1 is connected to the active node through a SIP trunk. The office route selection code is automatically created after a distributed network is configured.
ϒ⁄The office route selection code is 253(X1911/X1960)or 1022 (X1981) when local node 1 is connected to the standby node through a SIP trunk. The office route selection code is automatically created after a distributed network is configured.
ϒ⁄Choose Trunk > Office Route Configuration > Office Route Selection Code and click Create.
ϒ⁄Set Office Route Selection Code to 0.
ϒ⁄Click OK.
2.Set office route IDs.
ϒ⁄Both the office route selection code and the office route ID are 0 when local node 1 connects to the PSTN through a PRA trunk.
ϒ⁄The office route ID is 252(X1911/X1960)or 1021 (X1981) when local node 1 is connected to the active node through a SIP trunk. The office route ID is automatically created after a distributed network is configured.
ϒ⁄The office route ID is 253(X1911/X1960)or 1022 (X1981) when local node 1 is connected to the standby node through a SIP trunk. The office route ID is automatically created after a distributed network is configured.
ϒ⁄Choose Trunk > Office Route Configuration > Office Route and click Create.
ϒ⁄Set Office route ID to 0, and select 0 from the Office route selection code drop-down list box.
ϒ⁄Click OK.
3.Configure a number change index.
ϒ⁄Digit deletion: Configure number change index 0, which is used to delete the first digit of called numbers.
ϒ⁄Number change: Configure number change index 1, which is used to change the calling number to the automatic switchboard number 28885999 of the headquarters.
ϒ⁄Choose Trunk > Office Route Configuration > Number Change Index and click Create.
ϒ⁄Configure number change index 0.
ϒ⁄Click OK.
ϒ⁄Click Create. Configure number change index 1.
ϒ⁄Click OK.
Configuring Prefixes
1.Configure intra-office call prefix 8.
a.Choose Trunk > Called Prefix Configuration and click Create.
b.Configure intra-office call prefix 8.
c.Click OK.
2.Configure outgoing call prefixes.
a.Prefix for users at branch 1 to make outgoing calls: 900, 90, and 9
b.Prefix for users at the headquarters and branch 2 to make outgoing calls through branch 1: 90571
c.Click Create. Configure international toll call prefix 900.
![]()
Local call prefix 9 can be configured only after international toll call prefix 900 and national toll call prefix 90 are configured.
d.Click OK.
Configure other prefixes by using the same method. The interfaces for configuring other prefixes are similar to Figure 8. Table 1 describes the differences.
Table 1 Parameters for configuring outgoing call prefixes
Prefix |
Call Attribute |
Office Route Selection Code |
Calling Number Change |
Called Number Change |
900 |
International toll call |
0 |
1 |
0 |
90 |
National toll call |
0 |
1 |
0 |
9 |
Local call |
0 |
1 |
0 |
90571 |
Local call |
0 |
1 |
0 |
3.Configure local regeneration prefix 2888.
The prefix (2888 in this example) of long numbers on the local node needs to be configured as the local regeneration prefix. If long numbers in format of 3999XXXX are planned onsite, set 3999 as the local regeneration prefix.
a.Click Create and configure local regeneration prefix 2888.
![]()
In a two-node active/standby network, the system reroutes calls to the standby node if the active node is unreachable.
b.Click OK.
Configuring the SIP Trunk
After the central node is added, the system automatically creates the SIP trunk. If the U1980 functions as the local node, you need to perform the following steps to manually create the SIP trunk in versions earlier than V200R003C20SPC200; in V200R003C20SPC200 and later versions, the system automatically creates the SIP trunk. Configure the SIP trunk that connects local node 1 to the active node and standby node. Set the office route ID to 252 and 253, domain name of the peer device to DefDNPrimarySrv and DefDNStandbySrv, and SIP port number to 5060. In addition, enable the heartbeat function and set the interval for sending heartbeat messages to 120s.
1.Use an administrator account to log in to the web management system of a X1900 series unified gateway.
2.Choose Trunk > Trunk Configuration > SIP.
The connection between the local office and the peer office is displayed.
3.Click the line between 252 and local. Set the SIP trunk that connects local node 1 to the active node.
![]()
The outgoing call rights for the SIP trunk from the local node to the active node are inter and local by default. If a local node user needs to make national toll calls and international toll calls, add the outgoing national toll call right (ddd) and outgoing international toll call right (idd) for the SIP trunk. The command is config modify trunkgroup no x restrict yes outgoingright inter&loca&ddd&idd, where the variable x is the trunk group ID of the SIP trunk, which can be obtained using the show trunkgroup command.
4.Click OK.
Repeat the preceding steps to configure the SIP truck that connects local node 1 to the standby node.
Configuring the PRA Trunk
1.Choose Trunk > Trunk Configuration > PRA and click Add A Peer Office.
A red line is displayed between local and point0.
2.Click the line between local and point0.
3.Click Create and configure the PRA trunk.
4.Click OK.
The line between local and point0 turns green.
5.Choose System > Clock Source Configuration.
6.Set the peer device as the clock source to avoid frame slip (voice packet loss).
7.Click OK.
Configuring the Call Source for the Local Regeneration Prefix
1.Choose Trunk > TrunkGroup Configuration, as shown in Figure 13.
Figure 13 Viewing the trunkgroup
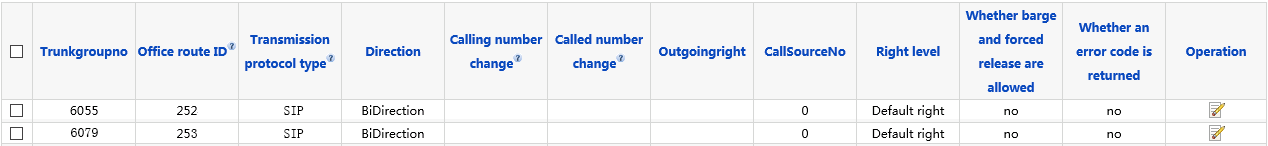
The office route ID is 252 and the value of Trunkgroupno is 6055 when local node 1 connects to the active node through a SIP trunk. The office route ID is 253 and the value of Trunkgroupno is 6079 when local node 1 connects to the active node through a SIP trunk.
2.Add call source 1.
a.Choose Trunk > CallSource and click Create.
b.Add callsource no 1.
3.Add SIP trunks from the local node to the central node to call source 1.
a.Choose Trunk > CallSource and click ![]() next to the trunkgroup 6055 and set CallSourceNo to 1.
next to the trunkgroup 6055 and set CallSourceNo to 1.
Add SIP trunk 6079 from the local node to the central node to call source 1 in the same way.
4.For calls from call source 1, enable the local node to change the call attribute of local regeneration prefix 2888 from localinter to inter, so that the local node will process such calls.
This configuration is used to process calls made to analog long numbers at the local node, preventing cyclic routing of the calls between the local node and central node.
a.Choose Trunk > CallSource and click ![]() next to the local regeneration prefix 2888.
next to the local regeneration prefix 2888.
Configuring Automatic Switchboards
This topic uses the default automatic switchboard as an example to describe how to configure the automatic switchboard. For more information about automatic switchboard with custom announcements, cyclical automatic switchboard, and automatic switchboard for dialing the switchboard number and extension number together, and local node voice playback, see Automatic Switchboard.
After the automatic switchboard is configured at the local node, the local node can process calls from the automatic switchboard during local regeneration in the event of a network fault between local and central nodes.
VU scripts of the automatic switchboard have been pre-configured into the system by default. Users can configure the automatic switchboard access code to enable automatic switchboard functions.
1.Use an administrator account to log in to the web management system of a X1900 series unified gateway.
2.Choose Trunk > Called Prefix Configuration and click Create.
3.Set the automatic switchboard access code and use the default values of other parameters.
4.Click OK.
Configuring IP Phones
The method for configuring IP phones at branches is similar to that for configuring IP phones at the headquarters. For details, see Allocating Numbers to SIP Users.
Differences: When configuring IP phones at branches, configure the active node, standby node, and local node as SIP servers.
Configuring IADs
The method for configuring IADs at branches is similar to that for configuring IADs at the headquarters. For details, see Allocating Numbers to SIP Users.
Differences: When configuring IADs at branches, configure the active node, standby node, and local node as SIP servers.
Parent Topic: Configuring the Unified Gateway Two-Node Cluster