Navigation: Fault Management > Troubleshooting Guide > Trunk Faults > Background >
The primary rate adaptation (PRA) trunk signaling process varies according to the user type.
Basic Concept
Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
It has 30B+D and 23B+D type. Both B channels and D channels are 64 kbit/s digital channels. Except for the United States, all countries use 30 B channels and one D channel.
Signaling Process
A SIP user in unified gateway calls a user in peer device, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Normal signaling process for a call initiated by a SIP user
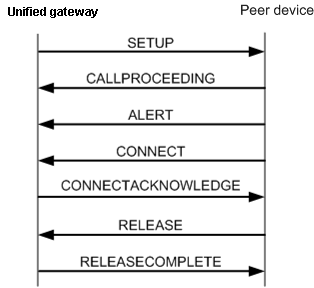
The signaling process is described as follows:
1.When an intra-office user calls an peer user, unified gateway sends a SETUP message, requesting to set up a call.
2.Peer device returns a CALLPROCEEDING message, indicating that the call is being set up.
3.Peer device sends an ALERT message, indicating that the phone of the peer user rings.
4.Peer device sends a CONNECT message, indicating that the peer user picks up the phone.
5.unified gateway sends a CONNECTACKNOWLEDGE message, indicating that the intra-office has learned that the peer user has picked up the phone.
6.The intra-office user starts to talk with the peer user.
7.Peer device sends a RELEASE message, indicating that the peer user hangs up.
8.unified gateway sends a RELEASECOMPLETE message, indicating that the intra-office user hangs up. unified gateway and peer device release channel resources.
![]()
If the intra-office user is callee user, the signaling process is oppositional.
Parent Topic: Background