Navigation: Configuration > Configuration Guide (Web Mode) > Configuring Toll Fraud Prevention >
This section describes how to configure call attributes for a call prefix, call-out right for call transfer through a trunk, maximum number length for the automatic switchboard, and call-out right for call transfer through the VU to prevent outer-office users from making outgoing calls through the unified gateway or VU.
Background
All prefixes have a basic call attribute, which can be one of the following:
ϒ⁄inter: intra-office call right.
ϒ⁄local: local call right.
ϒ⁄ddd: national toll call right.
ϒ⁄idd: international toll call right.
In addition to basic call attributes, you can configure 32-level customized rights for prefixes.
All users or trunks have certain outgoing call rights, which can be one or multiple of the preceding four basic call attributes and 32-level customized rights. By default, users and trunks have the inter and local outgoing call rights.
When a user makes an outgoing call, the gateway obtains the intersection of outgoing call rights of the user or trunk and the call attributes of the matched prefix. If the intersection is empty, the call is restricted. If the intersection is not empty, the call is allowed.
Figure 1 shows the trunk tandem network.
Figure 1 Trunk tandem network
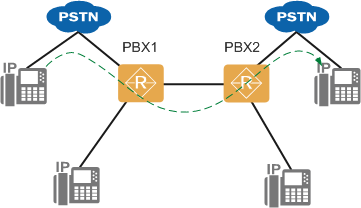
In this scenario, the outgoing call rights for a VU prefix, outgoing call rights for a trunk, and rights for an outgoing prefix are used as the criteria for calls that are again routed outside the office. The outgoing call rights for a VU prefix specify the outgoing call rights of users who dial the automatic switchboard number and then have two-stage dialing. The outgoing call rights for a trunk specify the rights of calls that are routed into the office and then routed outside the office again. The rights for an outgoing prefix specify the rights for calls routed outside the office from an intermediate office.
The relationships among the VU outgoing call rights for an automatic switchboard number, outgoing call rights for a trunk, and call attributes of a prefix are as follows (Assume that the call attribute of the outgoing prefix for making calls from PBX-1 to PBX-2 is local):
ϒ⁄If a PSTN user dials the automatic switchboard number of PBX-1 and then dials an outgoing prefix and the phone number of a user under PBX-2 as prompted, the VU outgoing call rights for the automatic switchboard number of PBX-1 and the outgoing call rights for the trunk from PBX-1 to PBX-2 contain the local call right of the outgoing prefix.
ϒ⁄If a PSTN user places a call to PBX-1 and PBX-1 transfers the call to PBX-2 according to the called number prefix, the outgoing call rights for the trunk from PBX-1 to PBX-2 contain the local call right of the outgoing prefix.
Configuring Call Attributes for Prefixes
When you control outgoing call rights of users by configuring prefixes, pay attention to the following:
1.Prefix rights must be distinguished clearly. That is, prefixes with lower rights cannot contain prefixes with higher rights. For example, a prefix with the local call right cannot contain a prefix with the ddd call right.
2.Configure the minimum outgoing call rights for users based on the service requirements.
The following assumes that the local call, national toll call, and internal toll call prefixes for outgoing calls from the PBX1 to PSTN are 9, 90, and 900 respectively. When a user dials 9 + international toll number, the gateway matches outgoing prefix 900 because an international toll number generally starts with 00. The gateway determines that the user does not have international toll call rights and restricts the call. This prevents toll fraud.
Common toll fraud mode: A user dials 9 + nest dialing prefix of the carrier (such as 17900, 17901, 17909, 17911, 17951, 10193, 12593, 197, 11808) + international toll number to make an outgoing call.
Prevention measure:
1.Confirm all dialing modes that will be considered as international toll calls with the carrier.
![]()
You must confirm all nest dialing prefixes for international toll calls with the carrier, and configure the rights of these prefixes on the gateway to prevent toll fraud.
2.Configure international toll prefixes required by services as idd prefixes.
3.If there are international toll prefixes that are not required by services, ask the carrier to restrict the outgoing call rights of these prefixes. If the carrier cannot restrict the outgoing call rights of these prefixes, configure rights that no intra-office user has for these prefixes.
![]()
When an enterprise determines that the international toll call service is not required, you are advised to request the carrier to reject all international toll calls initiated from the enterprise.
4.On the gateway, configure prefix 9 as a local prefix, 9 + nest dialing prefix + 0 as a national toll prefix, and 9 + nest dialing prefix + 00 as an international toll prefix.
For example, when an intra-office user dials 9 + 17909 + international toll number, the gateway matches international toll prefix 91790900. The gateway determines that the user does not have international toll call rights and restricts the call. This prevents toll fraud.
Configuration example: All calls with call numbers starting with 00, 1790900, 1180800, 462600, and 44000 are considered as international toll calls. The carrier cannot restrict the outgoing call rights of these prefixes. Users always dial prefix 9 to make outgoing calls to the PSTN. When making international toll calls, users always dial prefix 900 or 917909. The idd prefixes should be configured as follows:
ϒ⁄9: local
ϒ⁄90: ddd
ϒ⁄900: idd
ϒ⁄91790900: idd
ϒ⁄91180800: cus31. Use 32-level customized rights to control outgoing calls. No intra-office user has the cus31 outgoing call right.
ϒ⁄No prefix for outgoing calls to the PSTN starts with 4.
The following describes how to configure prefixes 9, 90, 900, 917909, 9179090, and 91790900.
1.Configure the number change index 1:the first digit of the number is deleted.
config add predeal index 1 changetype delete changepos 0 changelen 1
2.Set the call attribute of prefix 900, 91790900 to idd.
config add prefix dn 900 callcategory basic callattribute idd cldpredeal yes cldindex 1 officeselectcode 3 minlen 0 maxlen 32
config add prefix dn 91790900 callcategory basic callattribute idd cldpredeal yes cldindex 1 officeselectcode 3 minlen 0 maxlen 32
3.Set the call attribute of prefix 90 to ddd.
config add prefix dn 90 callcategory basic callattribute ddd cldpredeal yes cldindex 1 officeselectcode 2 minlen 0 maxlen 13
4.Set the call attribute of prefix 9 to local.
config add prefix dn 9 callcategory basic callattribute local cldpredeal yes cldindex 1 officeselectcode 1 minlen 0 maxlen 12
5.Set the call attribute of prefix 91180800 to idd and cus31.
config add prefix dn 91180800 callcategory basic callattribute idd&cus31 cldpredeal yes cldindex 1 officeselectcode 1 minlen 0 maxlen 32
![]()
You have to configure the ddd prefix and idd prefix before you configure the local prefix.
Configuring Outgoing Call Rights for Trunks
Outgoing call rights for a trunk include inter, local, ddd, idd, and 32-level customized call rights. You can configure multiple outgoing call rights for a trunk. By default, a trunk has the local call rights. If you want to forbid the outgoing call rights for trunk tandem calls through a trunk, you are advised to configure only the inter call right for the trunk so that an outer-office user who makes an incoming call through the trunk cannot make a call to another outer-office user. To allow an outer-office user who makes an incoming call through the trunk to make a local call, you can use the default setting. To allow an outer-office user who makes an incoming call through the trunk to make a national or international toll call, you must add the ddd or idd call right to the trunk.
The following describes how to configure the inter call right for a primary rate access (PRA) trunk:
1.Configure the inter call right for the PRA trunk whose GroupNo is 26.
config modify trunkgroup no 26 restrict yes outgoingright inter
![]()
ϒ⁄The call rights for a trunk limit the outgoing call rights for trunk tandem calls only. The common outgoing calls for internal users are not affected.
ϒ⁄If a trunk has local or more call rights, a user who makes an incoming call through the trunk can then make a call to an outer-office number, which brings the toll fraud risk.
Configuring a Number Length Limit for the Automatic Switchboard
When configuring the automatic switchboard, modify related parameters in the automatic switchboard script if the extension number length cannot exceed 4 digits, as shown in Figure 2. For details about how to configure the automatic switchboard, see Product Documentation > Configuration > Feature Guide > Automatic Switchboard.
Figure 2 Configuring the extension number length
![]()
Configuring VU Outgoing Call Rights
VU outgoing call rights for an automatic switchboard number include inter, local, ddd, idd, and 32-level customized call rights. You can configure multiple VU outgoing call rights for an automatic switchboard number. By default, an automatic switchboard number has the inter call right.
The following describes how to configure the inter call right for automatic switchboard number 28980808:
1.Configure the inter call right for automatic switchboard number 28980808.
config add prefix dn 28980808 callcategory vu callattribute vuconsole vuoutgoingright inter cldpredeal no
![]()
If an automatic switchboard number has local or more call rights, users can dial the automatic switchboard number and then an outer-office number as prompted to make an outgoing call, which brings the toll fraud risk.
Parent Topic: Configuring Toll Fraud Prevention