Navigation: Fault Management > Troubleshooting Guide > Login and Registration Faults > Analog Phone Directly Connected to the Unified Gateway >
Login and registration do not apply to analog phones.
After numbers are configured on the X1900 unified gateway, the analog phones can be used once they are connected to the X1900 unified gateway.
The ASI/OSU boards on the X1900 unified gateway are used to connect analog phones.
ϒ⁄Each ASI board provides 32 FXS ports for connecting 32 analog phones.
ϒ⁄Each OSU board provides 12 FXS ports for connecting 12 analog phones. It also provides 12 FXO ports, which are used to connect analog trunks.
On the X1900 unified gateway, a POTS number is configured for each FXS port and the analog phones are directly connected to these FXS ports using phone cables (high-density subscriber cables).
The analog phone number is the POTS number of the corresponding FXS port.
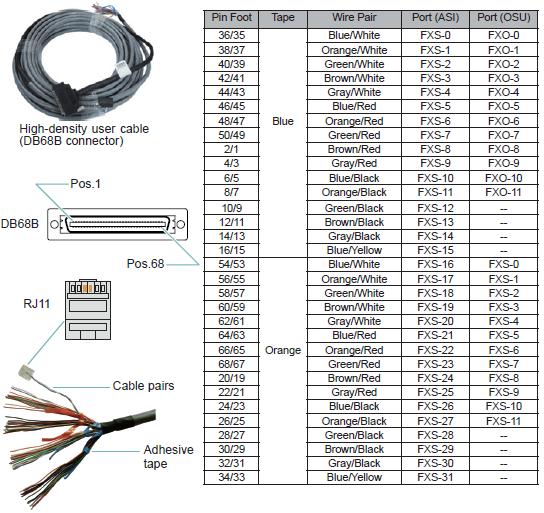
A high-density subscriber cable consists of four cable clusters, with each cluster bundled with blue or orange adhesive tapes. Each cable cluster has eight twisted pairs, and each pair has two cores in different colors. Each pair corresponds to an FXS port. You can identify the mappings between twisted pairs and FXS ports by color, based on which you can know the analog phone numbers.
Figure 1 Pin assignments of a high-density subscriber cable
Parent Topic: Analog Phone Directly Connected to the Unified Gateway