Navigation: Fault Management > Troubleshooting Guide > Login and Registration Faults > Analog Phone Under the IAD >
The method of rectifying the fault that the analog phone fails to register with the IAD is the same as the method of rectifying the fault in the scenario where the analog phone is directly connected to the unified gateway.
Here, we just focus on the faults that may occur during the interaction between the IAD and the unified gateway.
Possible Causes
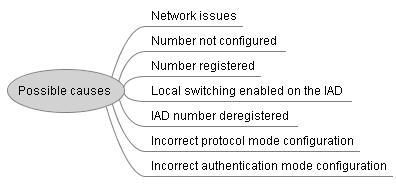
Troubleshooting Methods
Enable port mirroring on the IAD, and use Wireshark to trace the SIP messages exchanged between the IAD and the X1900 unified gateway.
![]()
Command to enable port mirroring on the IAD: monitor 1 observing-port 2
This command is used to enable the function of copying data from network port 1 (source port) to network port 2 (destination port).
ϒ⁄If the IAD sends registration messages, check the response messages on the X1900 unified gateway.
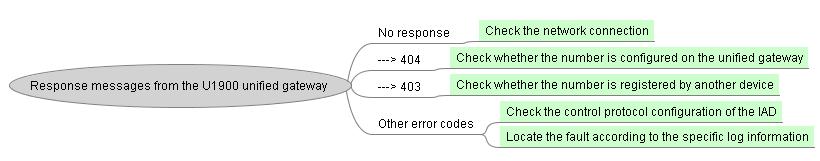
ϒ⁄If the IAD does not send registration messages, check whether local switching is enabled on the IAD or whether the number is deregistered.
Troubleshooting Common Faults
Fault 1: connection issues
Verify the network cable connection between the IAD and the unified gateway.
Verify the cable connection between the IAD and the analog phone.
Fault 2: The corresponding number is not configured.
Verify that the corresponding SIP number is configured on the unified gateway.
Verify that the SIP number is configured on the corresponding port of the IAD.
Fault 3: The user number has been registered on another device.
Rectifying the fault by referring to "Fault 8: The user number has been registered" in Troubleshooting Common Faults.
Fault 4: Local switching has been enabled on the IAD.
When disconnected from the unified gateway, the IAD automatically enters the local switching state.
When the network between the IAD and the unified gateway recovers, the IAD does not initiate registration to the unified gateway but stays in local switching state.
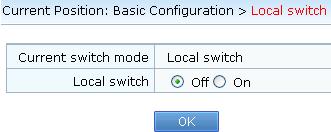
Log in to the web management system of the IAD, and choose Basic Configuration > Local Switch. On the page that is displayed, disable local switching.
Fault 5: The number on the IAD has been deregistered.
Run the undo sip shutdown {all | <user-SN>} command to cancel the number deregistration operation.
Fault 6: The control protocol used by the IAD for interacting with the unified gateway is different from that used by the unified gateway.
The IAD can interact with the unified gateway using either the MGCP or SIP protocol.
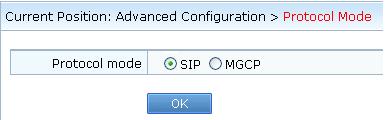
Log in to the web management system of the IAD, and choose Advanced Configuration > Protocol Mode. On the page that is displayed, change the protocol to be the same as that configured on the unified gateway.
Fault 7: The SIP user authentication mode configured on the IAD does not match the configuration on the connected network.
A network to which the IAD is connected authenticates users either by user ID or by user name.
The authentication mode relies on the telecom carrier of the network. The IMS network uses authentication by user name. For other networks, authentication by user ID is generally used.
Log in to the web management system of the IAD, and choose SIP Service Configuration > Soft Parameter. On the page that is displayed, change the authentication mode to be the same as that configured on the connected network.
Parent Topic: Analog Phone Under the IAD