Navigation: Fault Management > Troubleshooting Guide > Login and Registration Faults > Analog Phone Under the IAD >
Analog phones are connected to the IAD using phone cables, and the IAD is then connected to the X1900 unified gateway using a network cable.
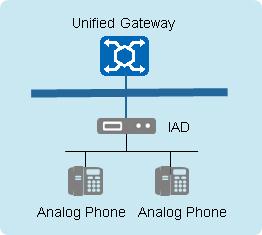
For the X1900 unified gateway, IADs are SIP terminals, just like IP phones. SIP numbers configured on the X1900 unified gateway are then configured on the IAD, and the IAD interacts with the unified gateway over the IP network.
The interaction between the IAD and the X1900 unified gateway is similar to that between the IP phone and the unified gateway.
Numbers corresponding to the FXS ports are configured on the IAD, and they have a one-to-one mapping relationship with the SIP numbers configured on the X1900 unified gateway. During a call, the IAD converts analog signals sent from the analog phone into digital signals, and sends the digital signals to the X1900 unified gateway. The interaction between the IAD and the analog phone here is similar to that between the unified gateway and the analog phone that is directly connected to the unified gateway.
The Register message sent from the IAD to the X1900 unified gateway carries the user ID (corresponding to the SIP user on the X1900 unified gateway) and the IP address of the IAD. The X1900 unified gateway uses these two parameters to uniquely identify a
The Contact header field carries the user ID as well as the IP address and port number of the IAD, the value of Expires is the registration interval, and the User-Agent header field carries the IAD version information.
Parent Topic: Analog Phone Under the IAD