Navigation: Fault Management > Troubleshooting Guide > Login and Registration Faults > IP Phone >
IP phones register with the X1900 unified gateway through the IP network.
1.SIP numbers are allocated on the X1900 unified gateway.
2.The IP address and port number of the X1900 unified gateway (that is, the SIP server) and the number are configured on the IP phone.
3.The IP phone sends a registration request to the X1900 unified gateway.
Interactions Between the IP Phone and the X1900 Unified Gateway
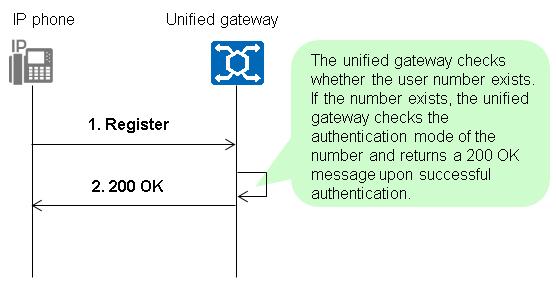
IP Phone Registration Process
1.The IP phone sends a registration request to the X1900 unified gateway (that is, the SIP server).
The request message contains the SIP number as well as the IP address and port number of the IP phone.
Regardless of the authentication mode for the SIP number, the request message does not contain the authentication information when the IP phone initiates registration for the first time.
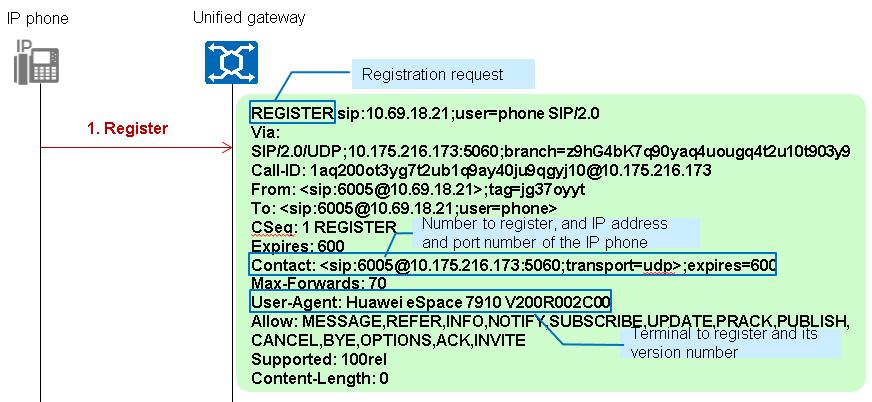
2.The X1900 unified gateway, according to the To header field in the registration request, checks whether the SIP user information stored on the control board contains this SIP number.
ϒ⁄If the SIP number does not exist, the X1900 unified gateway returns a "404 Not Found" message.
ϒ⁄If the SIP number exists, a binding relationship between the SIP number (IP phone number) and the X1900 unified gateway is set up.
3.The X1900 unified gateway determines whether this SIP number requires authentication according to the parameter settings of the SIP number.
![]()
The authentication mode is set during SIP number configuration on the X1900 unified gateway or BMU.
ϒ⁄No authentication
The X1900 unified gateway returns a 200 OK message, and the IP phone registration is successful. This mode has security risks and is not recommended.
ϒ⁄Authentication by IP address
The X1900 unified gateway matches the IP phone's IP address in the registration request's Contact header field with its trusted IP address. If they are matched, the X1900 unified gateway returns a 200 OK message; otherwise, the X1900 unified gateway returns a 403 Forbidden message, and the authentication fails.
ϒ⁄Authentication by password
1. The X1900 unified gateway returns a 401 Unauthorized message, asking the IP phone to send a registration request that carries the authentication information.
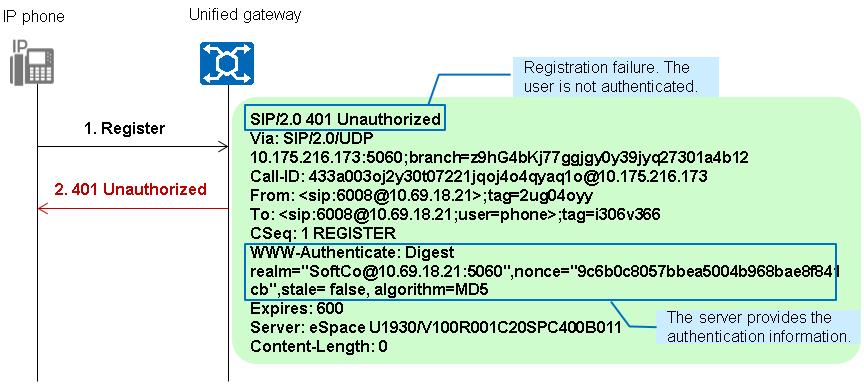 2. The IP phone sends a registration request that carries the authentication information.
2. The IP phone sends a registration request that carries the authentication information.
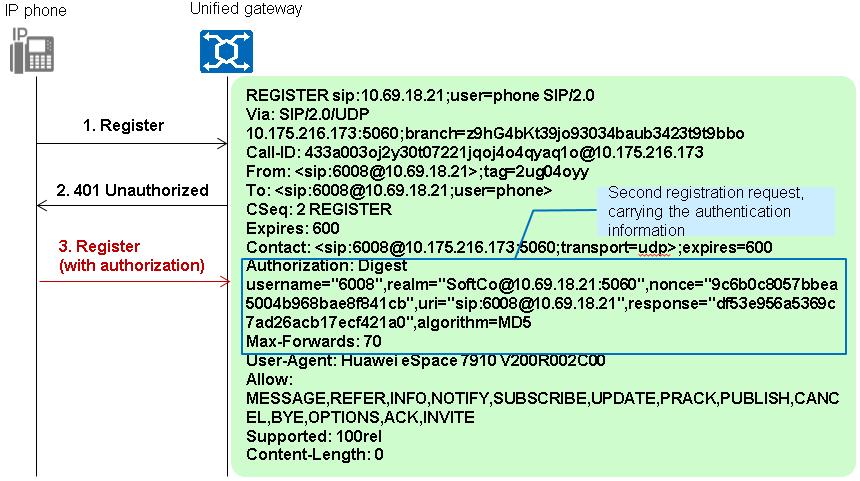
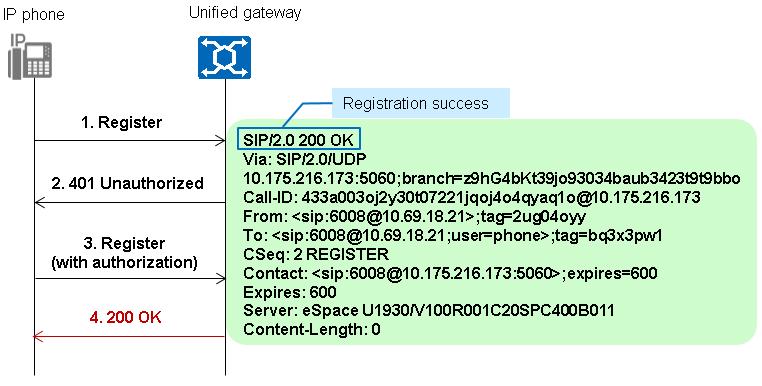
3. The X1900 unified gateway uses an irreversible encryption algorithm to check whether the ciphertext sent by the IP phone is the same as that stored on the unified gateway. If yes, the authentication is successful and the X1900 unified gateway returns a 200 OK message. If no, the authentication fails and the X1900 unified gateway returns a 403 Forbidden message.
The ciphertext sent by the IP phone and that stored on the unified gateway are both a string of characters that consist of the following fields encrypted using the MD5 algorithm: user number, password, and realm and nonce strings in the message. "Irreversible" means that others cannot deduce the password from this string of characters reversely.
ϒ⁄Authentication by password and IP addressBoth the IP address and the password are used for authentication.
Checking the Registration Status
Checking the registration status of IP phone users on the X1900 unified gateway
Log in to the web management system of the X1900 unified gateway as an administrator. Choose User > SIP User. In the Start Number text box, enter the number to query, for example, 81000, and click Search.

Status description:
ϒ⁄Idle: normal state
ϒ⁄Fault: not logged in
ϒ⁄If the number to query is not configured, no status is displayed.
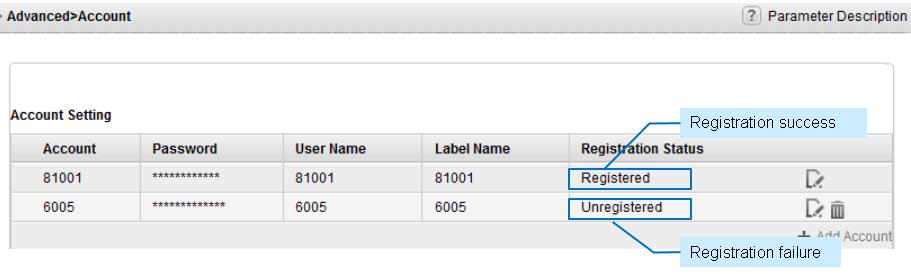
Checking the registration status on the IP phone
Log in to the IP phone. Choose Advanced > Account to check the registration status.
Recommended SIP registration period
On the IP phone management web page, the path for setting the parameter is: SIP Registration Cycle under Advanced > SIP Signaling.
In a two-node active/standby network, IP phones updates registration information to the standby node when the active node is faulty. Because the unified gateway receives a limited number of terminal registration requests every second, it is recommended that you set the IP phone registration period based on the terminal user capacity size, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Recommended SIP registration period
User Capacity Range |
10000~20000 |
5000~10000 |
1000~5000 |
500~1000 |
100~500 |
0~100 |
Recommended SIP registration period |
1200s |
600s |
360s |
300s |
240s |
150s |
Sequential Registration vs. Simultaneous Registration
ϒ⁄Sequential registration:
The IP phone sends registration messages to a SIP server at intervals of half of the registration interval. If the IP phone fails to register with the active SIP server, the IP phone registers with the standby SIP server. If the registration also fails, the IP phone registers with the local SIP server. Services are interrupted during the SIP server switching. After the IP phone registers with a SIP server successfully, its services become available again.
Services configured on the IP phone, for example, do not disturb, will be synchronized to the active SIP server and standby SIP server, but not to the local SIP server. The local SIP server is only used for local survival and ensures only basic voice calling.
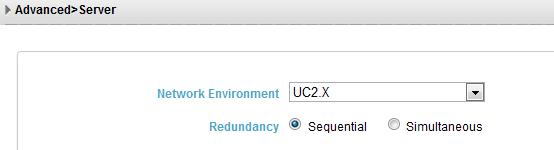
It is only used sequential registration in the UC2.X network environments.
After the IP phone is connected to the unified gateway, the connection information is automatically refreshed once every half of the registration interval to prevent connection timeout. If the connection times out, the unified gateway cancels its binding relationship with the SIP number, which will cause the faulty state of the SIP number.
ϒ⁄Simultaneous registration:
The IP phone registers with the active, standby, and local SIP servers at the same time. If the active SIP server fails, the standby SIP server takes over the services. If the standby SIP server also fails, the local SIP server takes over the services. The switching takes about 3s, which cannot be perceived by users. After the switching, services are running properly.
Simultaneous registration is used in the UC2.0 network environments.
Configuring the registration mode:
Access the web page of the IP phone as an administrator, and choose Advanced > Server.
In the configuration file of the IP phone, locate the DisasterRecoveryMode parameter in the Device > ComCfg > Phone > Environment path, and set the value to 0 (sequential) or 1 (simultaneous).
Parent Topic: IP Phone