SNMP Guide on Analog gateway
Introduction of SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an Internet-standard protocol for managing devices on IP networks. It is used mostly in network management systems to monitor network-attached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention. SNMP exposes management data in the form of variables on the managed systems, which describe the system configuration. These variables can then be queried (and sometimes set) by managing applications. The variables accessible via SNMP are organized in hierarchies, which are described by Management Information Bases (MIBs).
SNMP’s work progress
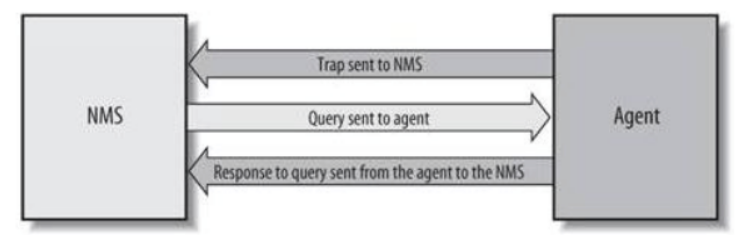
There are two components in SNMP called NMS and Agent.
NMS (Network Management Station) is the workstation that runs the client program. Currently, the commonly used network management platforms are QuidView, Sun NetManager, and IBM NetView.
Agent is the server-side software that runs on the network device.
The NMS can send GetRequest, GetNextRequest and SetRequest messages to the Agent. After receiving these request messages from the NMS, the Agent performs Read or Write operations according to the message type, generates Response messages, and returns the messages to the NMS.
The Agent also proactively sends a Trap message to the NMS when an abnormal condition or state change occurs in the device (e.g., device reboot) to report the event that occurred to the NMS.
SNMP uses the UDP protocol to transfer information between the manager and the agent. SNMP uses UDP port 161 to receive and send requests and port 162 to receive traps, which are required by default for devices performing SNMP. SNMP messages are all received on UDP port 161, and only trap messages are received on UDP port 162.
SNMP Version
Currently, the SNMP Agent in the device supports SNMP v3 version, which is compatible with SNMP v1 version and SNMP v2C version. SNMP v3 uses username and password authentication method.
SNMP v1 and SNMP v2C use Community name authentication, and SNMP messages with non-device recognized Community will be droped.
SNMP Community Name is used to define the relationship between SNMP NMS and SNMP Agent.The Community name acts like a password and can restrict SNMP NMS access to the SNMP Agent on the device.
The user can optionally specify one or more of the following characteristics associated with the community name.
- Define the MIB views that the community name can access.
- Set the community name’s access rights to the MIB object to read and write (write) or read-only (read). A group name with read-only permission can only query device information, while a community name with read-write permission can also configure the device.
- Set the basic access control list specified by the community name.
SNMP operation commands
The SNMP protocol is easy to use because it provides three basic operational commands for controlling MIB objects externally. They are: Get, Set and Trap.
- Get: The management station reads the value of the object at the agent. It is one of the most used commands in SNMP protocol because it is the basic way to get management information from network devices.
- Set: The station sets the value of the object at the agent. It is a privileged command because it can be used to change the configuration of a device or control the operational status of a device. It can set the name of a device, turn off a port or clear an entry in the address resolution table, etc.
- Trap: The agent proactively informs the management station of important events. Its function is to have the management agent notify the network management system that some special situation or problem has occurred without an explicit request from the network management system. In case of an unexpected situation, the client sends a message to port 162 of the server informing the server of a change in the value of a specified variable. Trap messages can be used to notify the management station of line failures, connection termination and restoration, authentication failures, and other messages. The management station can handle them accordingly.
MIB&OID
Management variables are used in SNMP messages to describe the management objects in the device.
To uniquely identify the managed objects in a device, SNMP uses a hierarchical naming scheme to identify the managed objects.
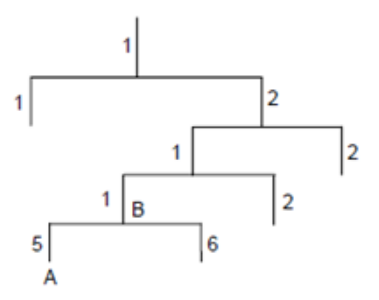
The entire hierarchy is like a tree, and the nodes of the tree represent management objects. Each node can be uniquely identified by a path starting from the root.
The MIB (Management Information Base) is used to describe the hierarchy of the tree, which is a collection of standard variable definitions for the monitored network devices.
In the figure below, managed object B can be uniquely identified by a string of numbers {1.2.1.1}, which is the Object Identifier (OID) of the managed object.
SNMP parameters description
The openvox analog gateway already supports three versions of SNMP functionality. They are typically SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
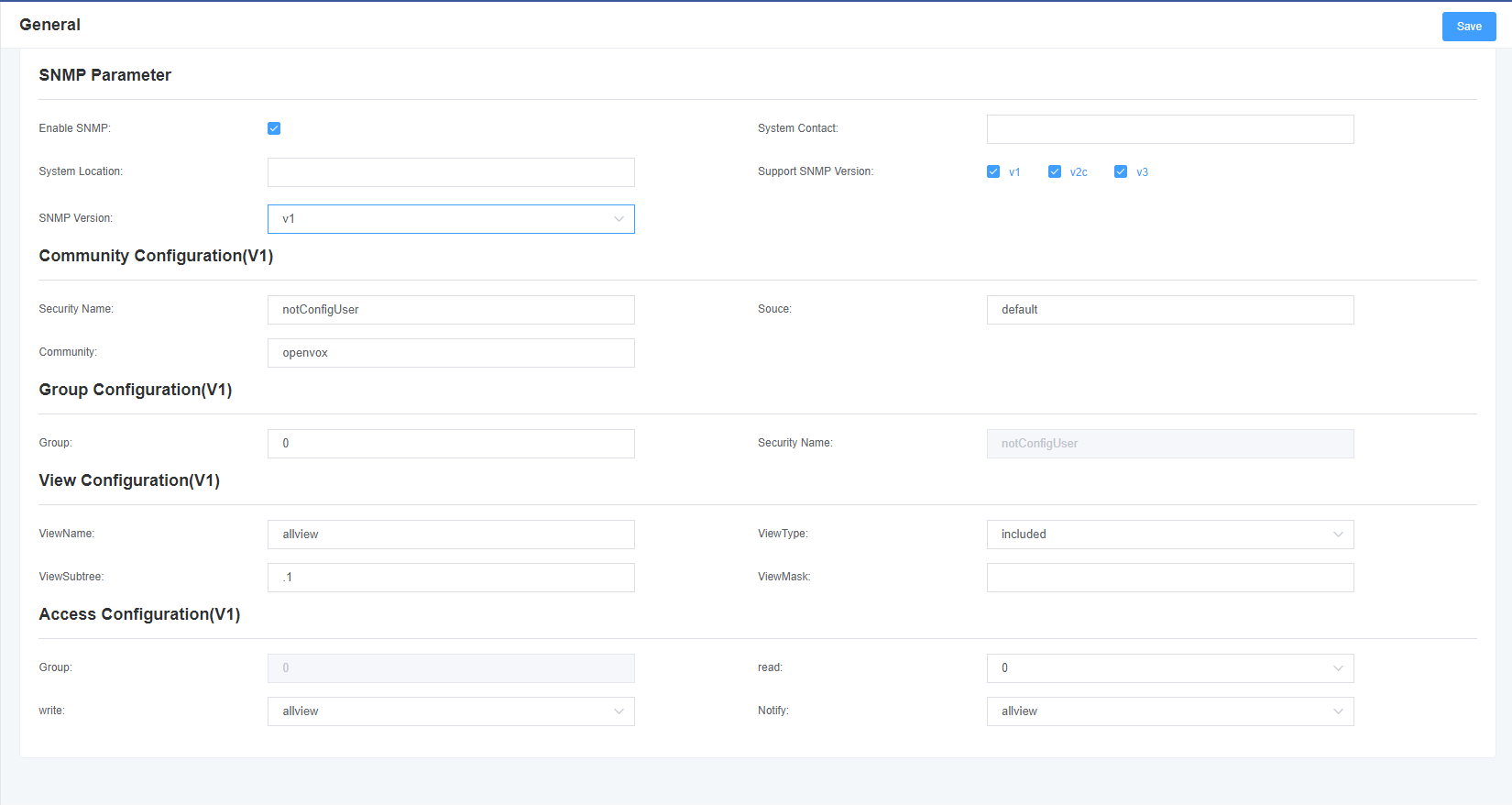
| Setting | Description |
| Enable SNMP | Enables/Disables the SNMP feature. Default settings is “No” |
| System Contact | System Contact |
| System Location | System Location |
| Support SNMP Version | Choose the SNMP version that support by device |
| SNMP Version | Choose the current SNMP version |
| Sercurity Name | Sercurity Name in the community |
| Souce | IP address range of NMS |
| Community | SNMP Community |
| Group | Device’s group |
| Viewname | SNMP Viewname |
| ViewType | Choose include/exclude the subtree in this view |
| ViewSubtree | Choose the MIB subtree in this view |
| Viewmask | Mask of the subtree(Hexadecimal) |
| Read | Read access |
| Write | Write access |
| Notify | Notify access |
In the SNMP v3, there are the following parameters that need special attention.
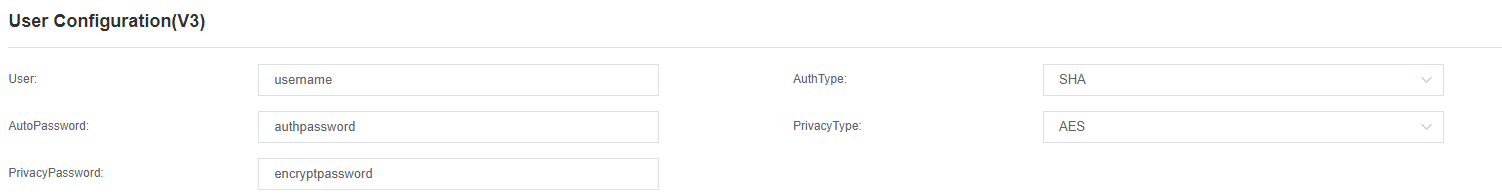
| Setting | Description |
| User | Username for SNMPv3 |
| AutoPassword | Enter the Authentication password |
| AuthType | Select the Authentication Protocol:
The default setting is “MD5” |
| PrivacyPassword | Enter the Privacy Key password |
| PrivacyType | Select the Privacy Protocol:
The default setting is “DES” |
SNMP Test
After configuring SNMP on client devices, you can test SNMP feature using your enterprise management system or a free SNMP test tool.
In this document we will be using “iReasoning MIB browser” which is a free and easy to use SNMP tester that include a Trap receiver.
You could get “iReasoning MIB browser” personal edition at http://ireasoning.com/download.shtml.
By using the “iReasoning MIB browser”, you could test SNMP funtion on openvox analog gateway easily.
Once the MIB file is imported into the MIB Browser, you can select different SNMP versions for verification.
Notice:To retrieve the MIB of openvox product, please Submit a technical support ticket to [email protected]
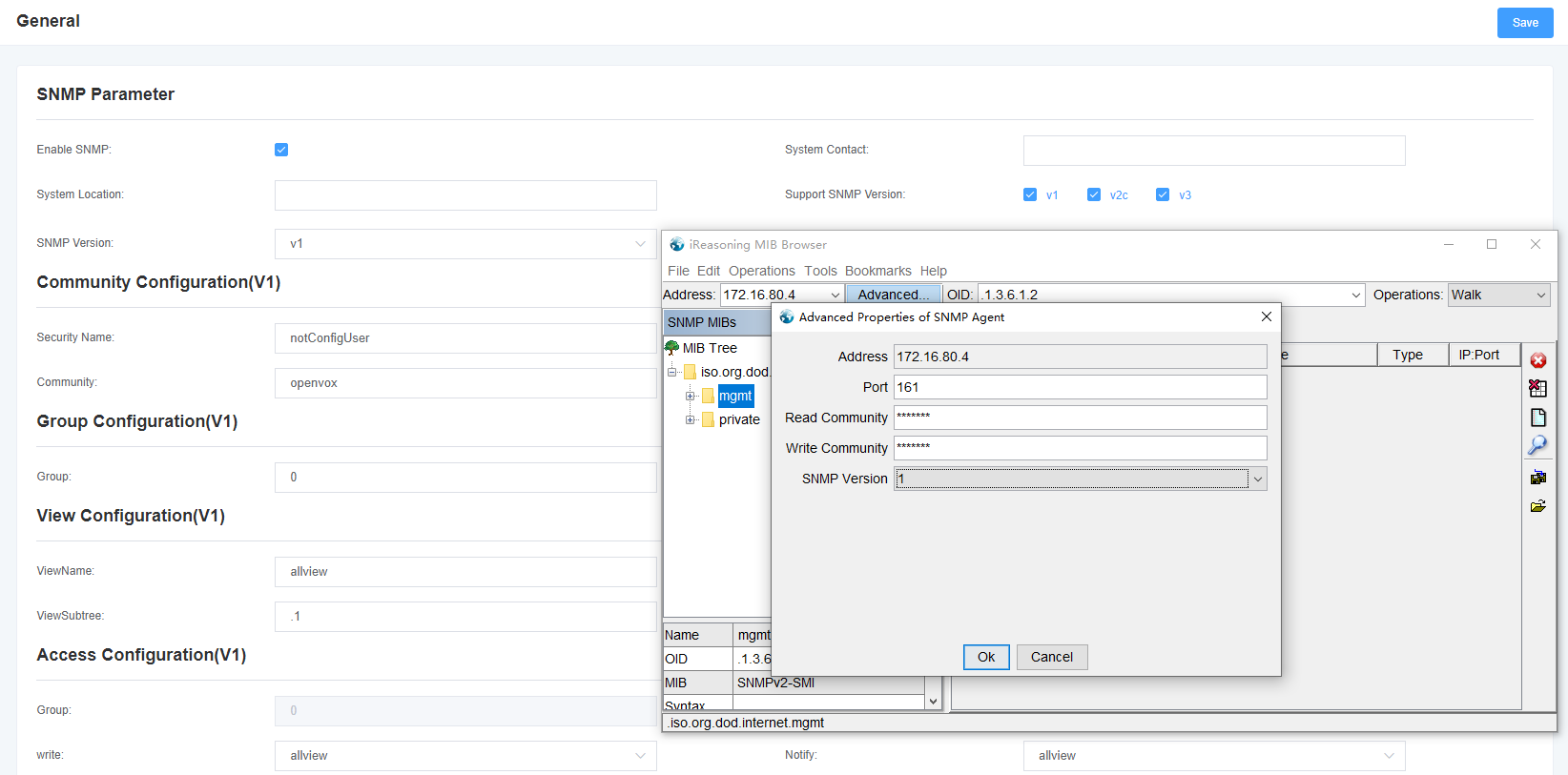
SNMP v1
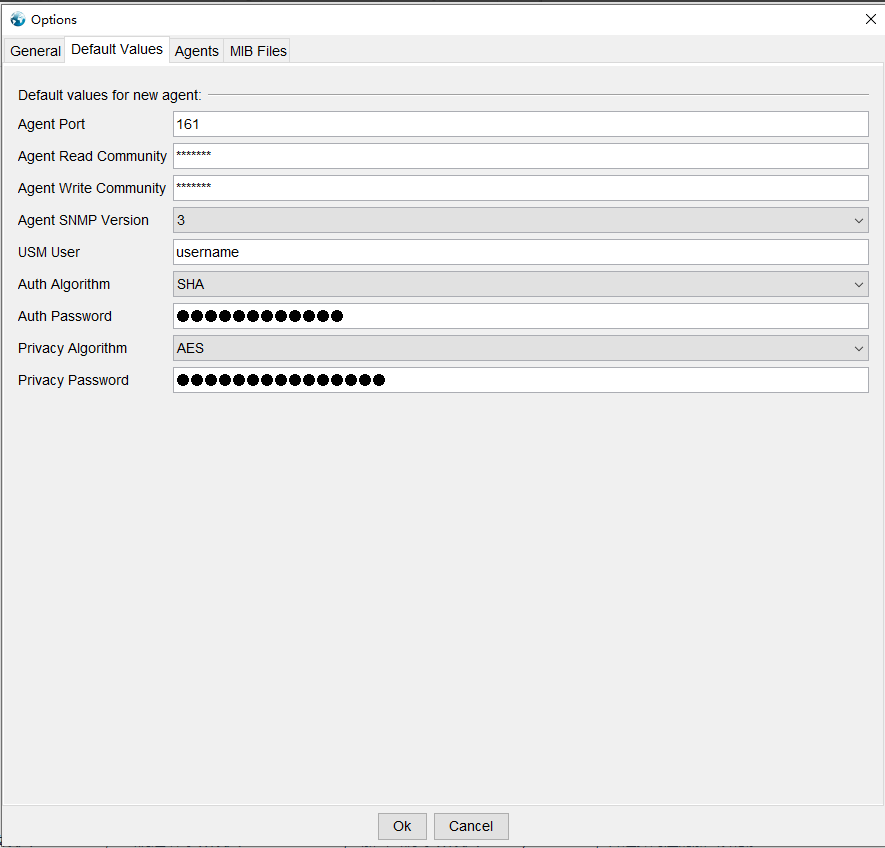
In the Analog Gateway SNMP page, select the version as v1. In the MIB Browser software, fill in the IP address of the device and the “Community” parameter to “Read Community” and “Write Community”, and set the SNMP Version to 1 and save it.
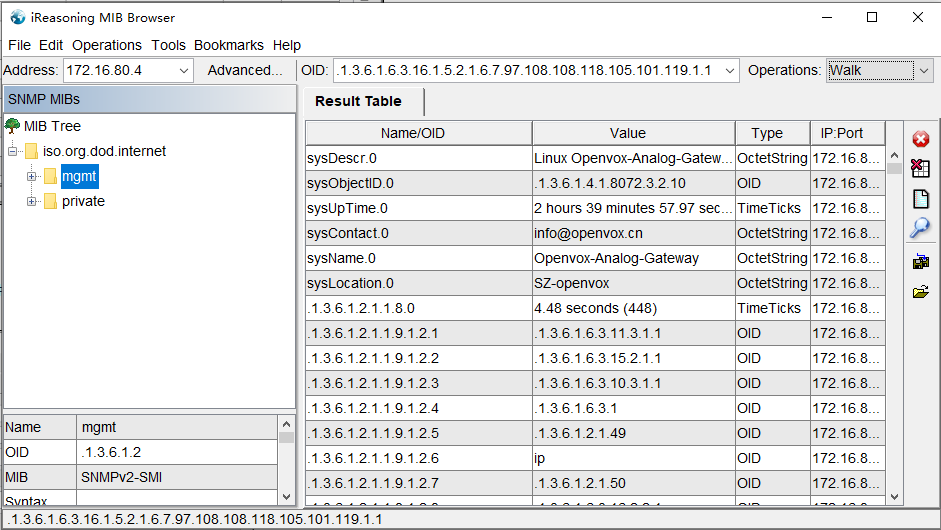
Select “walk” operation in MIB Browser, Value will output.
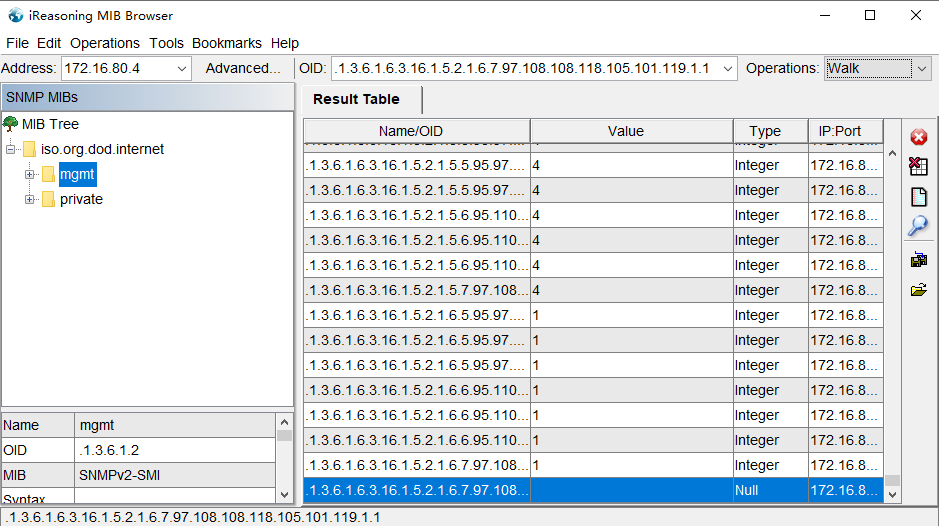
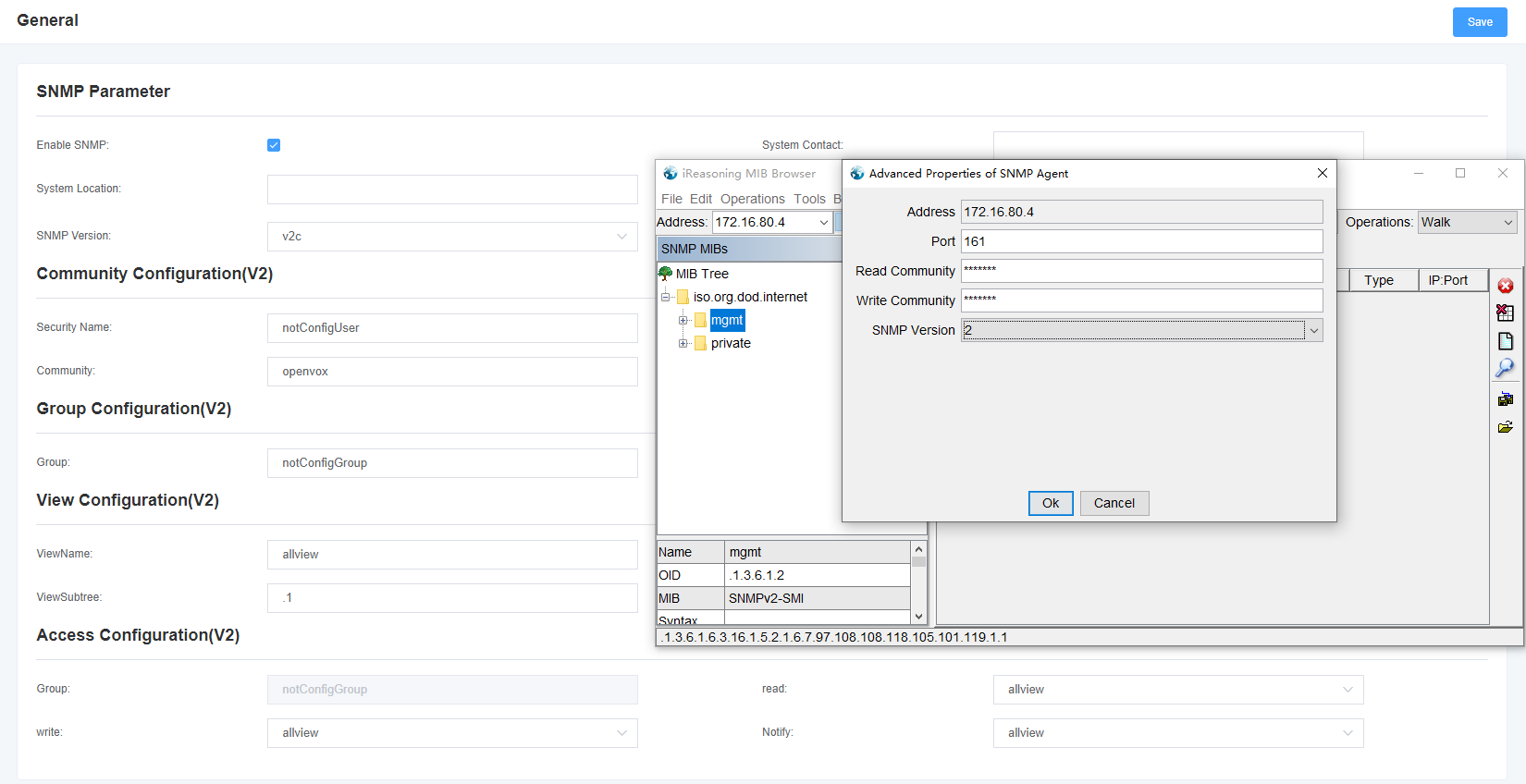
SNMP v2c
In the Analog Gateway SNMP page, select the version as v2c. In the MIB Browser software, fill in the IP address of the device and the “Community” parameter to “Read Community” and “Write Community”, and set the SNMP Version to 2 and save it.
Select “walk” operation in MIB Browser, Value will output.
SNMP v3
In the Analog Gateway SNMP page, select the version as v3. Open Tools-> Option->Default Values in MIB Browser software and select Version 3, fill in “USM User” for “User” parameter, “Auth Password” for “AuthPassword” parameter and “Privacy Password” for “PrivacyPassword” parameter, and select the corresponding encryption algorithm.