Hard disk recognition and boot mode selection in CCU
Hard disk recognition and boot mode selection in CCU
- CCU master module in UCP
The UCP platform currently supports four models of master control modules (CCUs):
| master module | CCU-N-BAYL | Intel Bay Trail quad-core processor |
| CCU-N-GML | Intel Celeron Gemini Laky Quad-Core Processor | |
| CCU-I-KABYLR | Intel Kaby Lake R i5 Quad-Core Processor | |
| CCU-I-TGL | 11th Generation Intel(R) Core(R) i5 Quad-Core Processor |
Among the above 4 CCUs, except for the latest CCU-I-TGL which only supports UEFI boot mode because it uses 11th generation Intel CPUs, the other 3 CCUs are compatible with both Legacy and UEFI boot modes.
- What is the difference between Legacy and UEFI boot modes?
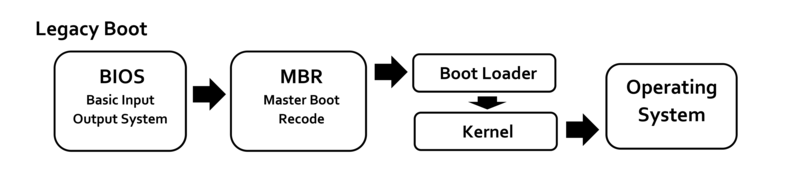
1. What is Legacy boot mode?
legacy boot mode is the boot process used by the BIOS firmware to initialize hardware devices. Legacy boot mode consists of a set of installed devices that are initialized when the computer performs a POST (Power On Self Test) test during the boot process. A legacy boot checks the master boot record (MBR) of all attached devices, usually located in the first sector of the disk. When it does not find a boot loader among the devices, Legacy switches to the next device in the list and repeats the process until it finds a boot loader, otherwise it returns an error.
2.What is UEFI boot mode?
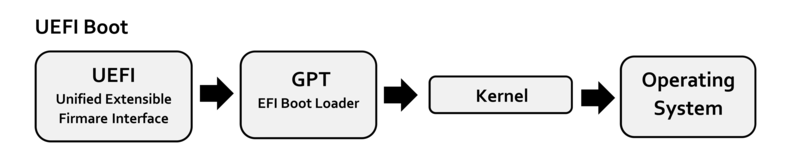
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a publicly available specification that defines the software interface between the operating system and the platform’s firmware.UEFI is the successor to the legacy PC BIOS and is intended to address its technical limitations.
It stores boot data in .efi files, not in the firmware. You will often find UEFI boot mode in newer motherboards.UEFI boot mode contains a special EFI partition that stores the .efi file and is used for the boot process and boot loader.UEFI uses the partitioned boot scheme of GPT to support larger hard drives. Since the BIOS self-test process is eliminated, the boot speed is faster.
3. What is the difference between UEFI and Legacy?
Although, UEFI and Legacy are very similar in terms of boot process. However, at a deeper level, they are different in many ways:
| UEFI boot mode | Legacy boot mode |
| UEFI provides a better user interface | Legacy boot mode is traditional and very basic |
| Uses the GPT partitioning scheme | Uses MBR partitioning scheme |
| UEFI provides faster boot times | It is slower compared to UEFI |
| Since UEFI uses GPT partitioning scheme, it can support up to 9ZB storage devices | The MBR partitioning scheme used by Legacy only supports up to 2TB storage devices |
| UEFI runs in 32-bit and 64-bit and supports mouse and touchpad | Legacy runs in keyboard-only, 16-bit-only mode |
| It allows for secure booting, preventing the loading of unauthorized applications It can also prevent dual-booting because it treats the operating system (OS) as an application |
He does not provide a secure startup method that allows unauthorized applications to be loaded, and does not restrict dual-boot |
| It has a simpler update process | It is more complex compared to UEFI |
Because UEFI boot mode has faster boot speed, better performance, better expandability and security, and high development efficiency, support for graphical interfaces, ease of use, the future of new hardware will gradually phase out the Legacy mode, only support for UEFI mode, Intel has confirmed that after the 11th generation of CPUs only support for UEFI mode, it is recommended that production environments in the Intel has confirmed that only UEFI mode will be supported after the 11th generation of CPUs.
- How to view hard disk information in BIOS?
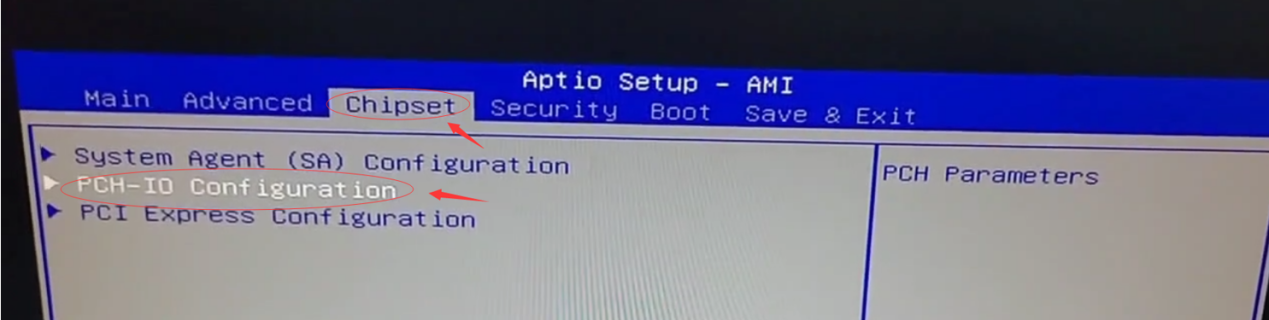
Regardless of which CCU model you have, the most accurate way to view the hard disk is to view the connected hard disk information in the storage controller. Keep clicking the DEL or ESC button after powering on the computer to access the BIOS setup screen, go to Chipset🡪 PCH-IO Configuration.
Find SATA And RST Configuration.
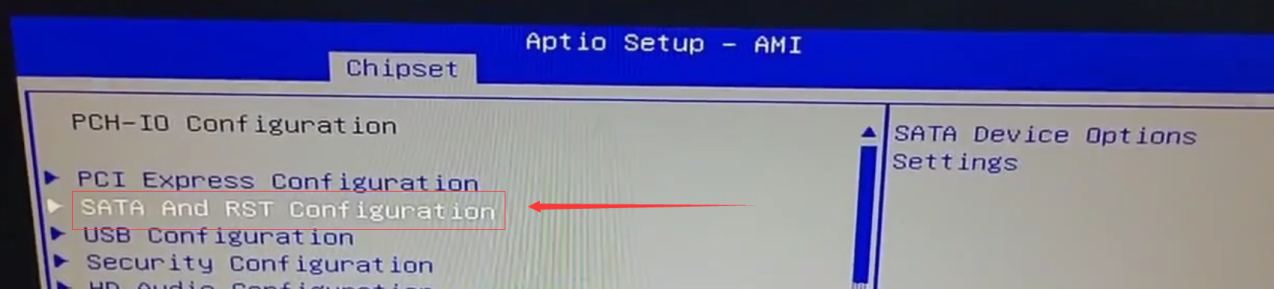
You can see that the CCU recognizes a Lenova SSD SL7 drive with a capacity of 256GB:
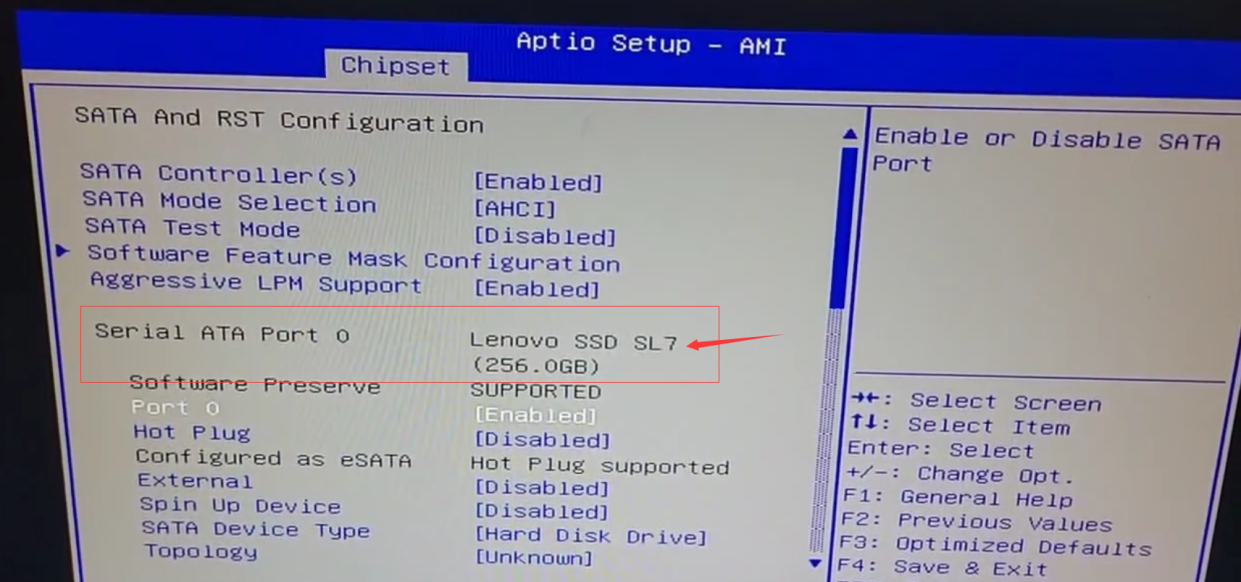
Once the hard disk is recognized, we can proceed with the installation of the operating system.
- How to select boot mode in BIOS?
1.Legacy and UEFI compatibility modes
Intel’s motherboards prior to the 11th generation CPUs were basically compatible with both Legacy and UEFI modes, so all three CCUs except the CCU-I-TGL will have a CSM configuration entry in the BIOS:
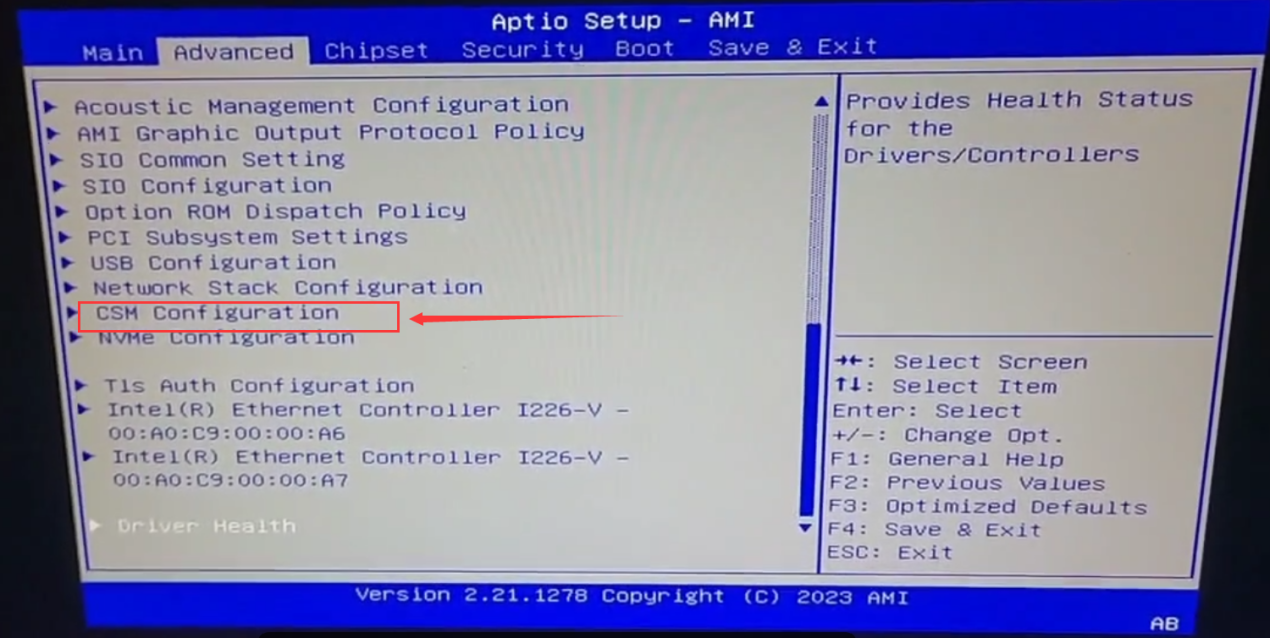
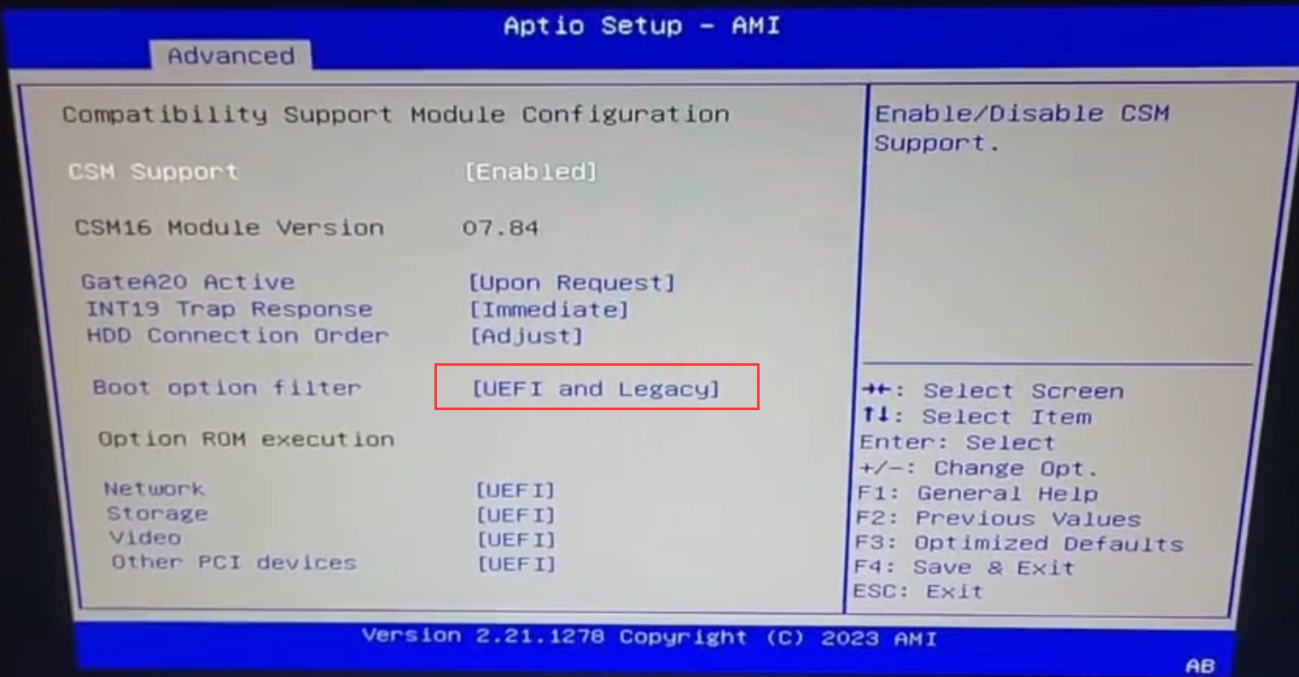
And it defaults to UEFI and Legacy compatibility mode:
In the Boot menu in this mode, there are usually two boot items for a hard disk. As shown in the figure below, the one with the UEFI mark in front is the UEFI boot mode, and the one without UEFI is the traditional Legacy boot mode:
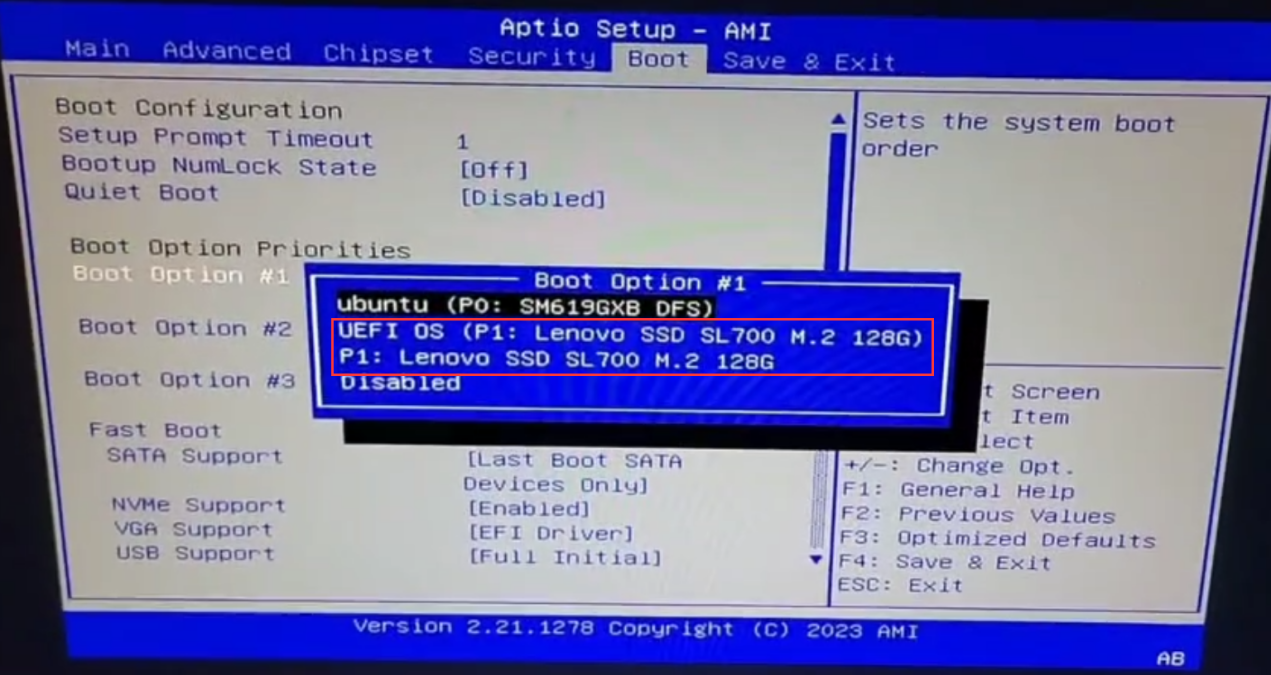
If you are not sure about the two modes, you will be confused to see this and not know which boot item is the right one to choose. Regarding the choice of Legacy or UEFI mode, you need to choose according to the actual situation. If the operating system to be installed supports UEFI mode, it is preferred to use UEFI boot mode; however, there are some older operating systems that do not support UEFI well or do not support UEFI boot mode at all, such as CentOS 6.x and earlier systems, then you should choose Legacy mode to boot the installation. You can specify whether to use Legacy or UEFI mode in the CSM configuration item, so that you can filter out the useless boot items in the Boot menu to avoid interference.
If the operating system you’re installing is in Legacy boot mode and you have multiple hard drives then be sure to keep an eye on the [Hard Drive BBS Priorities] option:
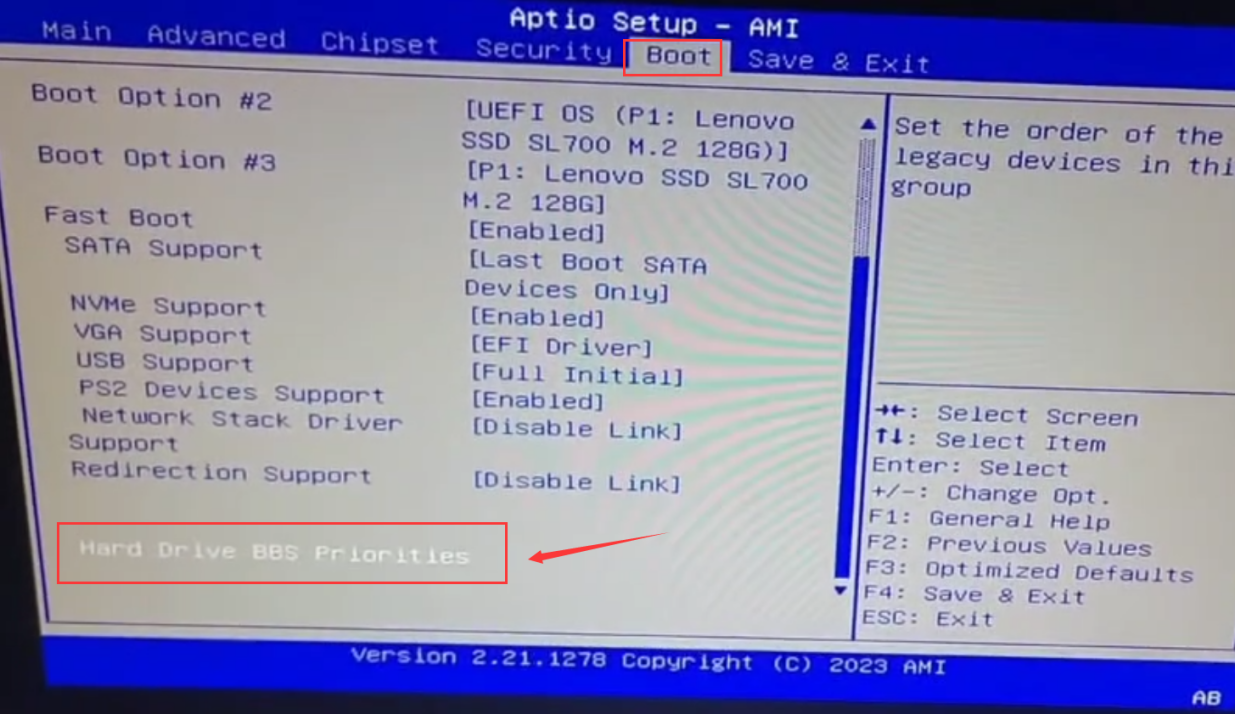
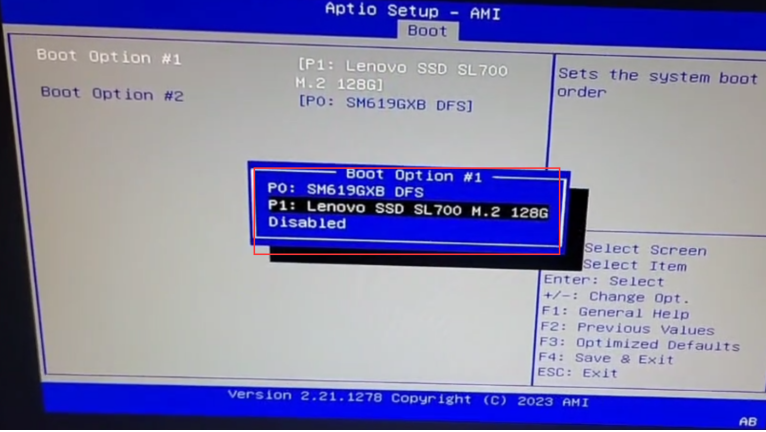
Please set the target disk where you install the system as the first boot item, otherwise you will not be able to enter the operating system.
If the operating system you want to install is in UEFI mode, set it to [UEFI only] mode:
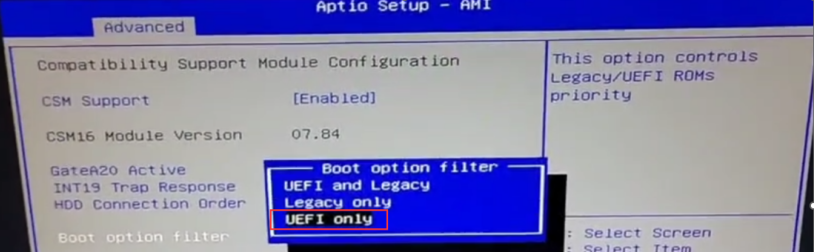
2.UEFI only mode
Intel only supports UEFI mode after the 11th generation CPU, so CCU-I-TGL also only supports UEFI mode, there will be no CSM configuration item in the BIOS (in the old version of the BIOS the CSM configuration item existed but didn’t work correctly, it has been removed in the new version), so you can only install an operating system that supports UEFI mode. In the Boot menu, you can only see boot devices that support UEFI, such as boot USB disks or CD-ROM drives that support UEFI. If it is a hard disk without a system installed or the system in the hard disk does not support UEFI, it will not show up in the Boot startup items either:
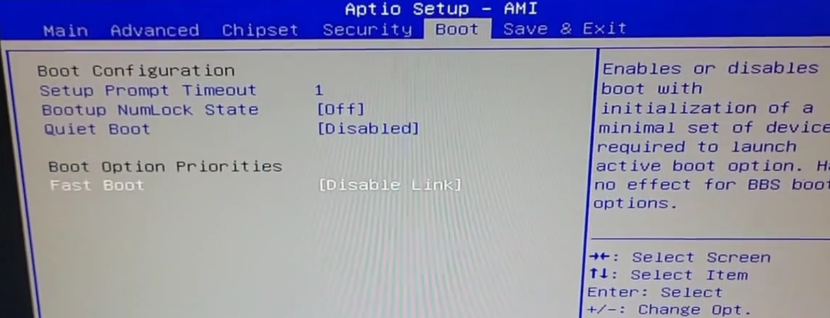
However, this does not mean that the drive is bad or unrecognizable, just that there is no UEFI boot file available on the drive.
For more information about hard disk recognition, please check the [How to View Hard Disk Information in BIOS] section above.
- The case of configuring CCU-I-TGL in UCP to install the domestic Unisys operating system UOS
1. When we have installed the hard disk, insert the created system boot USB flash drive, you can see the boot information of the USB flash drive in the Boot menu:
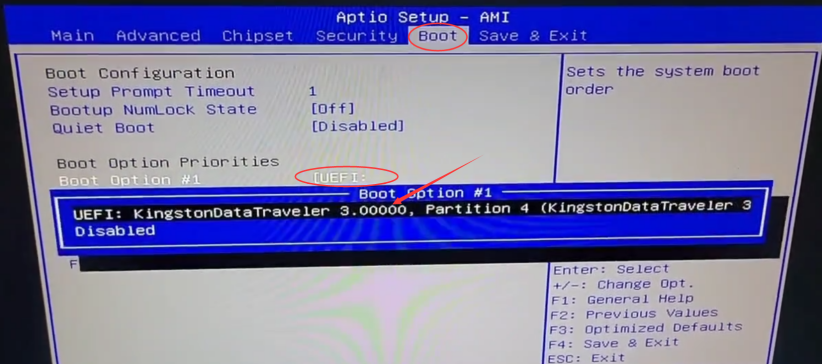
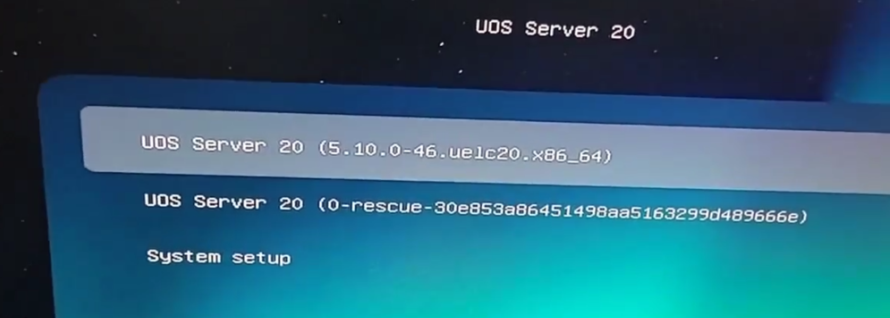
2.After setting it as the first boot item, rebooting will bring you to the UOS installation boot screen:
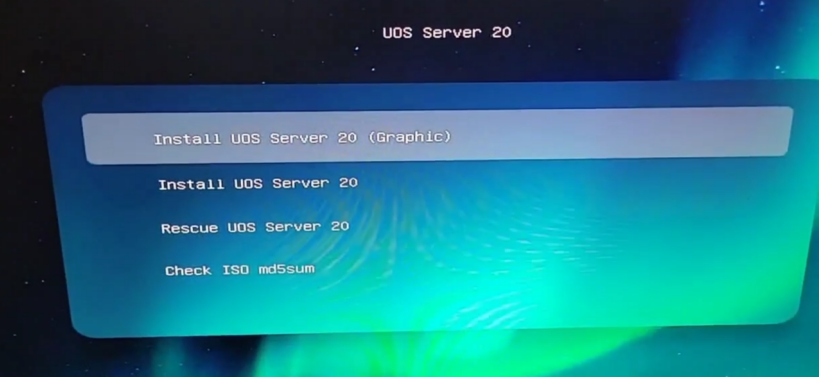
3.During the installation process you can see that the target disk is an optional previously installed Lenova SSD SL700, although it is not visible in the startup items, it does not affect the system installation:
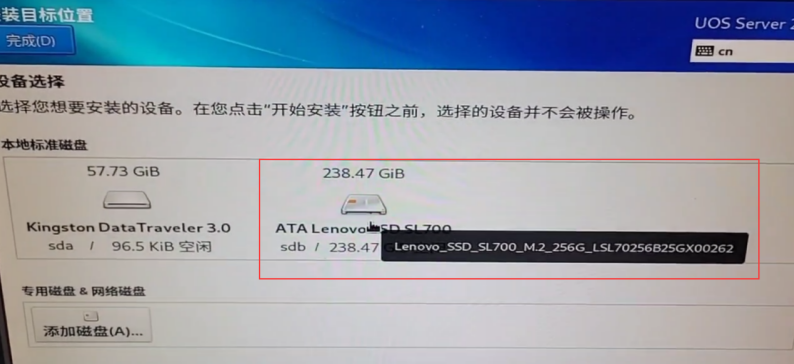
4.Once the system installation is complete, you can see the UEFI boot entry for UOS in the Boot menu:
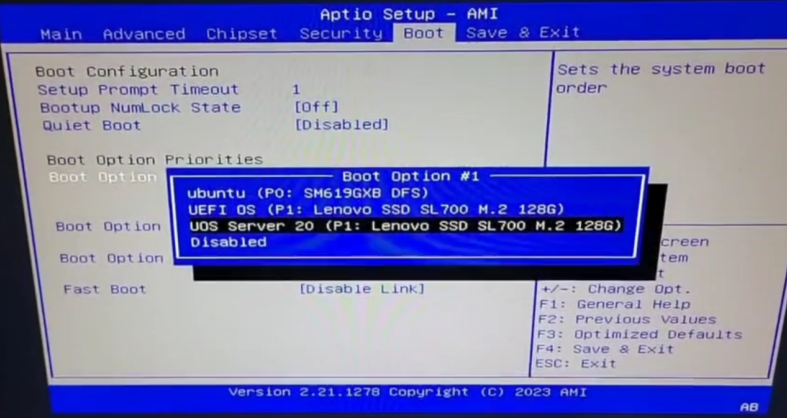
Set the boot entry beginning with UOS Server 20 as the first boot entry and reboot to the UOS operating system:.