The Application Demo Code for 4 kinds of Core Control Units on UCP
The Core Control Unit and Core Switch Unit on UCP
- The OpenVox UCP platform supports three types of CCU boards.
CCU-N-BAYL: CPU model J1900/N2930.
CCU-N-GML: CPU model N4120.
CCU-I-KABYLR: CPU model I5 8250U.
CCU-L-TGL: CPU model I5 1135G7
After each CCU board is installed into the UCP chassis, one of 3 network interfaces is accessed through the backplane to the ETH interface of the Core Switch Unit (CSU), and the other two network interfaces are displayed on the front panel, WAN and LAN, respectively.

- The UCP supports two types of CSU boards, the 100M Switching Board CSU-F and the 1000M Switching Board (CSU-G):
The correspondence between the network interface of the CCU board and the panel silkscreen
For historical reasons, the three motherboards were not designed with the order of the network interfaces (eth0, eth1, eth2) and the panel silkscreen (WAN, LAN, CSU-ETH) in mind, resulting in some confusion when configuring the network interfaces in the operating system, as shown in the following figure.

CCU-N-BAYL: the network interface on the CSU corresponds to eth0, and the WAN and LAN correspond to eth1 and eth2.
CCU-N-GML: the network interface on the CSU corresponds to eth1, and the WAN and LAN correspond to eth2 and eth0.
CCU-I-KABYLR: the network interface on the CSU corresponds to eth2, and the WAN and LAN correspond to eth0 and eth1.
CCU-L-TGL: the network interface on the CSU corresponds to eth0, and the WAN and LAN correspond to eth1 and eth2.
The Demo Code for 4 kinds of Core Control Units on UCP
In order to allow users to better understand and use these three motherboards, we will provide some simple demo codes to show you how to identify and configure the network and reset buttons on the motherboard, as well as to perform UCP slot number identification.
- CPU model identification, NIC and silkscreen matching settings, reset button, and slot number identification on the motherboard
/usr/sbin/base.sh
#!/bin/bash
############## UCP 3 cpu models check ##########################
function is_i5_8250U_cpu()
{
CPU=`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | cut -f2 -d: | uniq |grep "i5-8250U"`
if [ "x${CPU}" != "x" ]; then
echo 1
else
echo 0
fi
}
function is_n4120_cpu()
{
CPU=`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | cut -f2 -d: | uniq |grep "N4120"`
if [ "x${CPU}" != "x" ]; then
echo 1
else
echo 0
fi
}
function is_j1900_cpu()
{
CPU=`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | cut -f2 -d: | uniq |grep "J1900"`
if [ "x${CPU}" != "x" ]; then
echo 1
else
echo 0
fi
}
function is_n2930_cpu()
{
CPU=`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | cut -f2 -d: | uniq |grep "N2930"`
if [ "x${CPU}" != "x" ]; then
echo 1
else
echo 0
fi
}
function is_network_config_null()
{
nic_config=`ls -l /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts | grep ifcfg-eth`
if [ "x${nic_config}" != "x" ]; then
echo 0
else
echo 1
fi
}
############## UCP RST key and Network ##########################
IS_I5_8250U_CPU=$(is_i5_8250U_cpu)
if [ "x${IS_I5_8250U_CPU}" = "x1" ]; then
GPIO_RST_KEY=444
GPIO_BOARDID0=378
GPIO_BOARDID1=379
GPIO_BOARDID2=380
GPIO_BOARDID3=381
NIC_WAN="eth0"
NIC_LAN="eth1"
NIC_BACK="eth2"
CPU_MODEL="i5-8250U"
IS_UCP=1
fi
IS_N4120_CPU=$(is_n4120_cpu)
if [ "x${IS_N4120_CPU}" = "x1" ]; then
GPIO_RST_KEY=415
GPIO_BOARDID0=421
GPIO_BOARDID1=422
GPIO_BOARDID2=414
GPIO_BOARDID3=413
NIC_WAN="eth2"
NIC_LAN="eth0"
NIC_BACK="eth1"
CPU_MODEL="N4120"
IS_UCP=1
fi
IS_J900_CPU=$(is_j1900_cpu)
if [ "x${IS_J900_CPU}" = "x1" ]; then
GPIO_RST_KEY=361
GPIO_BOARDID0=465
GPIO_BOARDID1=467
GPIO_BOARDID2=468
GPIO_BOARDID3=469
NIC_WAN="eth1"
NIC_LAN="eth2"
NIC_BACK="eth0"
CPU_MODEL="J1900"
IS_UCP=1
fi
IS_N2930_CPU=$(is_n2930_cpu)
if [ "x${IS_N2930_CPU}" = "x1" ]; then
GPIO_RST_KEY=361
GPIO_BOARDID0=465
GPIO_BOARDID1=467
GPIO_BOARDID2=468
GPIO_BOARDID3=469
NIC_WAN="eth1"
NIC_LAN="eth2"
NIC_BACK="eth0"
CPU_MODEL="N2930"
IS_UCP=1
fi
NIC_NUM=`ls /sys/class/net |grep -v lo | grep -v dummy0 | wc -l`
############# check UCP Slot ID ##########################
if [ "x$IS_UCP" = "x1" ];then
GPIO_PORTS="$GPIO_RST_KEY $GPIO_BOARDID0 $GPIO_BOARDID1 $GPIO_BOARDID2 $GPIO_BOARDID3"
for port in ${GPIO_PORTS};do
if [ -f "/sys/class/gpio/gpio${port}/direction" ]; then
echo "GPIO ${port} enabled"
else
echo $port > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo in > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${port}/direction
fi
done
BITS0=$(cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio${GPIO_BOARDID0}/value)
BITS1=$(cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio${GPIO_BOARDID1}/value)
BITS2=$(cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio${GPIO_BOARDID2}/value)
BITS3=$(cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio${GPIO_BOARDID3}/value)
BOARD_SLOT_NO=$((($BITS3 << 3) | ($BITS2 << 2) | ($BITS1 << 1) | $BITS0))
if [ $BOARD_SLOT_NO -lt 3 ]; then
BOARD_SLOT_NO=$(( $BOARD_SLOT_NO + 1 ))
fi
else
NIC_WAN="eth0"
NIC_LAN="eth1"
NIC_BACK="eth2"
BOARD_SLOT_NO="none"
GPIO_RST_KEY="none"
IS_UCP=0
fi
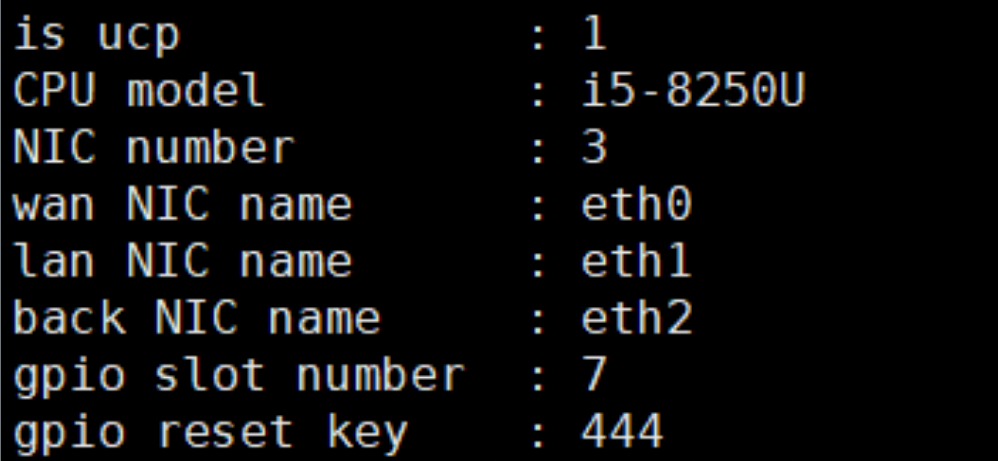
echo -ne "is ucp : ${IS_UCP}\n"
echo -ne "CPU model : ${CPU_MODEL}\n"
echo -ne "NIC number : ${NIC_NUM}\n"
echo -ne "wan NIC name : ${NIC_WAN}\n"
echo -ne "lan NIC name : ${NIC_LAN}\n"
echo -ne "back NIC name : ${NIC_BACK}\n"
echo -ne "gpio slot number : ${BOARD_SLOT_NO}\n"
echo -ne "gpio reset key : ${GPIO_RST_KEY}\n"
The variables obtained above will be used frequently in later practical applications.
The output of this script after execution is shown as follows.
- Easy-to-use network configuration tool
#!/bin/bash
#### Source the base.sh to get the variables
. /usr/sbin/base.sh
NIC_DIR=/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
WAN_CFG=$NIC_DIR/ifcfg-$NIC_WAN
LAN_CFG=$NIC_DIR/ifcfg-$NIC_LAN
BACK_CFG=$NIC_DIR/ifcfg-$NIC_BACK
function usage()
{
echo "Usage:"
echo -e "t $0 setip static addr netmask gateway wan|lan|back"
echo -e "t $0 setip dhcp wan|lan|back"
echo -e "t $0 setdns addr"
echo -e "t $0 reset network|all"
echo -e "t"
}
if [ "$#" -eq "2" -o "$#" -eq "3" -o "$#" -eq "6" ]; then
echo ""
else
usage `basename $0`
exit 1
fi
case "$1" in
###Set the IP mode to Static or DHCP
setip)
if [ x"$2" = x"static" ];then
addr=$3
netmask=$4
gateway=$5
nic=$6
if [ x"$nic" = x"wan" -o x"$nic" = x"lan" -o x"$nic" = x"back" ];then
if [ x"$nic" = x"wan" ]; then
nic_dev=$NIC_WAN
elif [ x"$nic" = x"lan" ]; then
nic_dev=$NIC_LAN
else
nic_dev=$NIC_BACK
fi
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=none"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$nic_dev"
echo "DEVICE=$nic_dev"
echo "IPADDR=$addr"
echo "NETMASK=$netmask"
echo "GATEWAY=$gateway"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
}>$NIC_DIR/ifcfg-$nic_dev
echo "IP Changed Successfully! Rebooting now ..."
/sbin/reboot
else
echo "NIC device $nic does not exist! NIC DevName must be wan, lan or back, please check and try again!"
exit
fi
elif [ x"$2" = x"dhcp" ];then
nic=$3
if [ x"$nic" = x"wan" -o x"$nic" = x"lan" -o x"$nic" = x"back" ];then
if [ x"$nic" = x"wan" ]; then
nic_dev=$NIC_WAN
elif [ x"$nic" = x"lan" ]; then
nic_dev=$NIC_LAN
else
nic_dev=$NIC_BACK
fi
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=dhcp"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$nic_dev"
echo "DEVICE=$nic_dev"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
}>$NIC_DIR/ifcfg-$nic_dev
echo "IP Changed Successfully! Rebooting now ..."
/sbin/reboot
else
echo "NIC device $nic does not exist! NIC DevName must be wan, lan or back, please check and try again!"
exit
fi
else
echo "NIC Mode is incorrect! It must be dhcp or static, please check and try again!"
exit
fi
;;
### Set the DNS
setdns)
if [ x"$2" != x"" ];then
addr=$2
{
echo "nameserver $addr"
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8"
echo -e "n"
}>/etc/resolv.conf
echo "DNS Changed Successfully! Rebooting now ..."
/sbin/reboot
else
echo "DNS server is null, please input a DNS server address!"
exit
fi
;;
### The API for reset action and other actions defined by users
reset)
### After networking reset, the IP address of ETH on CSU board will be 172.16.80.x/255.255.0.0, x is slot ID, WAN and LAN will be DHCP
if [ x"$2" = x"network" ];then
echo "Reset Network setttings to factory default ..."
rm $NIC_DIR/ifcfg-eth* -rf
if [ x"$NIC_WAN" != x"" ]; then
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=dhcp"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$NIC_WAN"
echo "DEVICE=$NIC_WAN"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
} > $WAN_CFG
fi
if [ x"$NIC_LAN" != x"" ]; then
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=dhcp"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$NIC_LAN"
echo "DEVICE=$NIC_LAN"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
} > $LAN_CFG
fi
if [ x"$NIC_BACK" != x"" ]; then
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=none"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$NIC_BACK"
echo "DEVICE=$NIC_BACK"
echo "IPADDR=172.16.80.${BOARD_SLOT_NO}"
echo "NETMASK=255.255.0.0"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
} > $BACK_CFG
fi
{
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8"
echo "nameserver 1.2.4.8"
echo -e "n"
}>/etc/resolv.conf
echo "Networking is factory default now! Rebooting ..."
/sbin/reboot
elif [ x"$2" = x"all" ];then
echo "Reset System to factory default ..."
##Customized script for Reset action, defined by users
#/usr/sbin/CUSTOM_SCRIPT
echo "Reset Network setttings to factory default ..."
rm $NIC_DIR/ifcfg-* -rf
if [ x"$NIC_WAN" != x"" ]; then
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=dhcp"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$NIC_WAN"
echo "DEVICE=$NIC_WAN"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
} > $WAN_CFG
fi
if [ x"$NIC_LAN" != x"" ]; then
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=dhcp"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$NIC_LAN"
echo "DEVICE=$NIC_LAN"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
} > $LAN_CFG
fi
if [ x"$NIC_BACK" != x"" ]; then
{
echo "TYPE=Ethernet"
echo "PROXY_METHOD=none"
echo "BROWSER_ONLY=no"
echo "BOOTPROTO=none"
echo "ONBOOT=yes"
echo "NAME=$NIC_BACK"
echo "DEVICE=$NIC_BACK"
echo "IPADDR=172.16.80.${BOARD_SLOT_NO}"
echo "NETMASK=255.255.0.0"
echo "NM_CONTROLLED=no"
echo -e "n"
} > $BACK_CFG
fi
{
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8"
echo "nameserver 1.2.4.8"
echo -e "n"
}>/etc/resolv.conf
echo "Networking is factory default now! Rebooting ..."
/sbin/reboot
else
echo "Reset nothing! Please check what you want to reset, network or all?"
exit
fi
;;
*)
usage `basename $0`
exit 1
esac
- RESET button identification and function definition
#!/bin/bash
#### Source the base.sh to get the variables
. /usr/sbin/base.sh
### Check the GOIP type, it is different between Old and New versions of Linux Kernel
function init_rstkey()
{
if [ -f /sys/class/gpio/export ]; then
echo "Old GPIO TYPE!"
GPIO_PIN=${GPIO_RST_KEY}
GPIO_PATH="/sys/class/gpio/gpio${GPIO_PIN}/direction"
echo ${GPIO_PIN} > /sys/class/gpio/unexport
sleep 1
echo ${GPIO_PIN} > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo in > $GPIO_PATH
elif [ -c /dev/gpiochip0 ]; then
echo "New GPIO TYPE!"
else
echo "GPIO not found!"
exit
fi
}
### Read the state of Reset GPIO key
function read_rstkey()
{
if [ -f /sys/class/gpio/export ]; then
RSTKEY_STATE=`cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio${GPIO_PIN}/value`
fi
if [ -c /dev/gpiochip0 ]; then
RSTKEY_STATE=`gpioget 0 10`
fi
}
### Define the Flags of short and long Press
function check_rstkey()
{
while :
do
sleep 0.5
read_rstkey
S_FLAG=0
L_FLAG=0
if [ x"${RSTKEY_STATE}" = x"0" ]; then
S_FLAG=1
sleep 3
read_rstkey
if [ x"${RSTKEY_STATE}" != x"0" ]; then
L_FLAG=0
break
else
sleep 3
read_rstkey
if [ "x${RSTKEY_STATE}" != x"0" ]; then
L_FLAG=0
break
else
L_FLAG=1
S_FLAG=0
break
fi
fi
fi
done
}
function main()
{
init_rstkey
check_rstkey
# echo "S_FLAG: $S_FLAG"
# echo "L_FLAG: $L_FLAG"
## Short Press is poweroff and Long press is reset
if [ "${S_FLAG}" = "1" ]; then
echo "`date` Power Key triggered, Power off System now ..."
sleep 0.5
#poweroff
else
echo "`date` Reset Key triggered, Restore System Settings ...."
sleep 0.5
#/usr/sbin/custom_reset_script
fi
}
main
The above demo codes basically demonstrate how to use the hardware functions of the UCP CCU board, and users are free to develop their own programs based on it.

